Results
61 Results found
Hourly data of CO2 emissions related to Swiss electricity mix
Abstract A new methodology was developed to assess the CO2 emissions of Swiss electricity considering: • High-temporal resolution of emission factors tied to consumed electricity in Switzerland. • Methodology based on market mechanism in order to identify the cross-border power plants providing the Swiss electricity imports. • Renewable share of consumed electricity based on physical flows, rather than commercial certificates (labels). A website was created with detailed information and daily/hourly data: https://horocarbon.ch Author: Romano, Elliot.
Abstract A new methodology was developed to assess the CO2 emissions of Swiss electricity considering: • High-temporal resolution of emission factors tied to consumed electricity in Switzerland. • Methodology based on market mechanism in order to identify the cross-border power plants providing the Swiss electricity imports. • Renewable share of consumed electricity based on physical flows, rather than commercial certificates (labels). A website was created with detailed information and daily/hourly data: https://horocarbon.ch Author: Romano, Elliot.

eRen Energy and Renovation
Abstract The eRen project proposes renovation solutions for the main typologies of the residential building stock of the French-Speaking part of Switzerland. The solutions consider a balance between energy efficiency, architectural protection, user comfort and costs while taking into account the building physics. Project partners: Hepia Genève, HEIG-VD, HES-SO Valais-Wallis, Fondations Immobilières de Droit Public, Gérances foncières SA, Fondation de placement immobilier Lithos, Retraites populaires. For more information: https://www.smartlivinglab.ch/fr/projects/eren-energie-et-renovation/ Authors: Schwab, Stefanie et al. Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.
Abstract The eRen project proposes renovation solutions for the main typologies of the residential building stock of the French-Speaking part of Switzerland. The solutions consider a balance between energy efficiency, architectural protection, user comfort and costs while taking into account the building physics. Project partners: Hepia Genève, HEIG-VD, HES-SO Valais-Wallis, Fondations Immobilières de Droit Public, Gérances foncières SA, Fondation de placement immobilier Lithos, Retraites populaires. For more information: https://www.smartlivinglab.ch/fr/projects/eren-energie-et-renovation/ Authors: Schwab, Stefanie et al. Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.
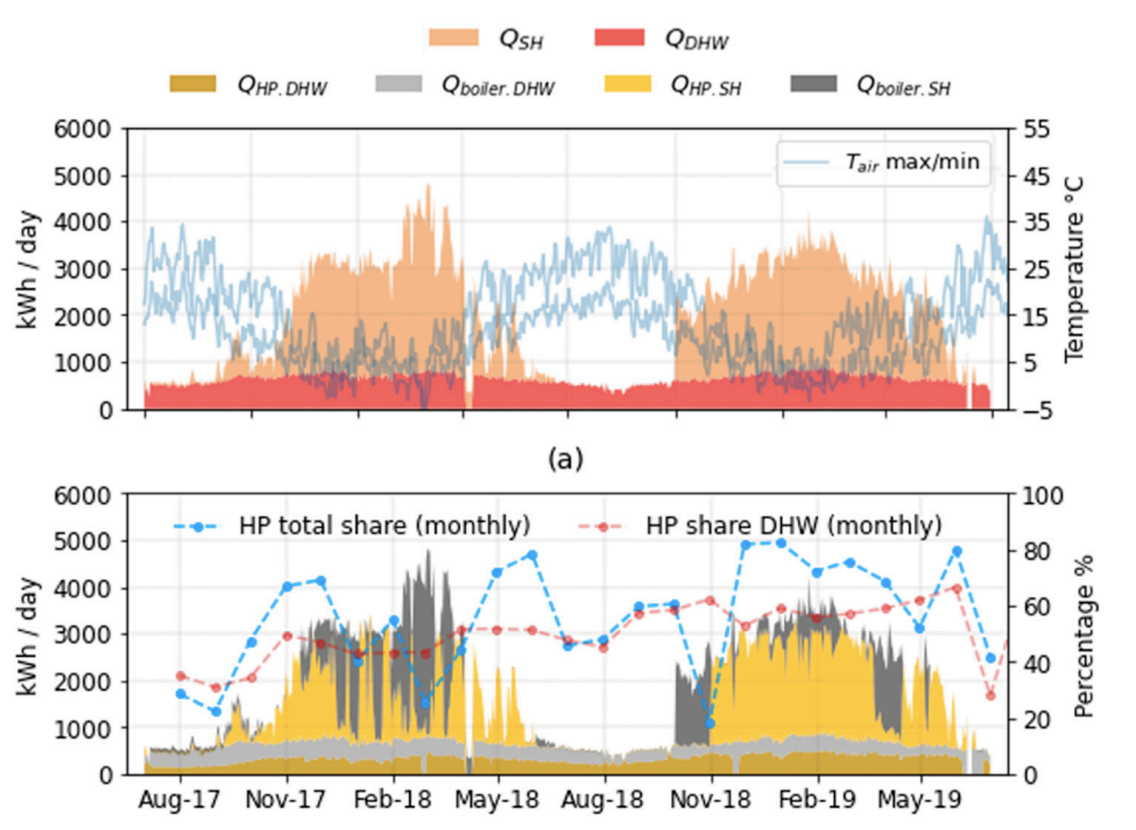
Large Air-to-Water Heat Pumps for Fuel-Boiler Substitution in Non-Retrofitted Multi-Family Buildings
Abstract The use of air source heat pumps (ASHP) in the specific context of existing multi-family buildings (MFB) represents an important challenge, especially in terms of performance and technical constraints in real conditions of use. This study concerns the actual performance of two non-retrofitted MFB (4047 and 7563 m2), whose original fossil heat supply was replaced by a centralized monovalent (2 × 156 kW) and hybrid (6 × 34 kW) ASHP system for space heating and domestic hot water. Based on a detailed monitoring campaign covering two years of operation, it can be concluded that both systems are able to supply the required temperature and cover the entire heat demand. By closely following up these pilot projects, constraints linked to integration and operation were identified. Optimization measures allowed us to increase the COP of the monovalent system (from 1.3 up to 3.4, with an optimized SPF of 2.3) and to raise the HP share of the hybrid system (from 50% to 67%, with an optimized SPF of 2.3). Both systems offer major progress in terms of CO2 savings (92% and 68%) and increased renewable energy share (75% and 43%), considering the hourly CO2 content of the Swiss electricity mix. Authors: Montero Dominguez, Omar et al.
Abstract The use of air source heat pumps (ASHP) in the specific context of existing multi-family buildings (MFB) represents an important challenge, especially in terms of performance and technical constraints in real conditions of use. This study concerns the actual performance of two non-retrofitted MFB (4047 and 7563 m2), whose original fossil heat supply was replaced by a centralized monovalent (2 × 156 kW) and hybrid (6 × 34 kW) ASHP system for space heating and domestic hot water. Based on a detailed monitoring campaign covering two years of operation, it can be concluded that both systems are able to supply the required temperature and cover the entire heat demand. By closely following up these pilot projects, constraints linked to integration and operation were identified. Optimization measures allowed us to increase the COP of the monovalent system (from 1.3 up to 3.4, with an optimized SPF of 2.3) and to raise the HP share of the hybrid system (from 50% to 67%, with an optimized SPF of 2.3). Both systems offer major progress in terms of CO2 savings (92% and 68%) and increased renewable energy share (75% and 43%), considering the hourly CO2 content of the Swiss electricity mix. Authors: Montero Dominguez, Omar et al.
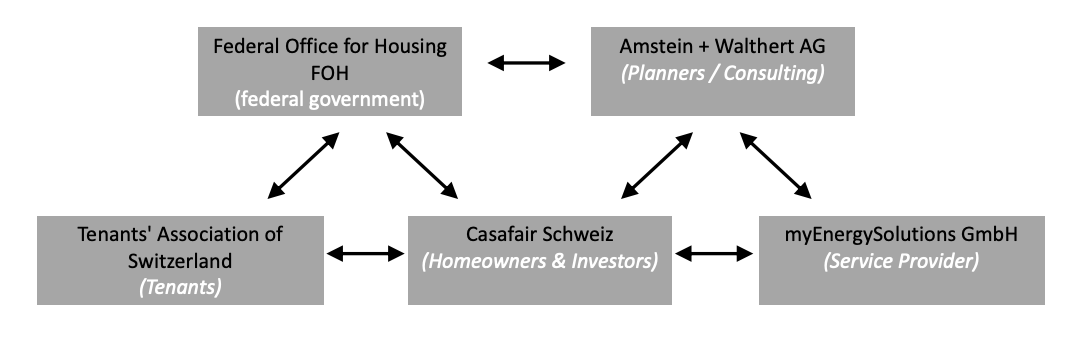
Monetization of qualitative impact factors
Abstract For rental properties, the share of value-adding investments in building renovations is of major importance, as these costs may be passed on to the rental. However, the distinction between this and the share of building maintenance covered by the current rent is complex and can be a barrier to such refurbishment projects. Due to the lack of practical instruments, an alternative calculation method “BKP-Triage” was defined together with the clients SFOE & FOH (Federal Office for Housing) and in exchange with partners HEV Schweiz & Tenants' Association. The results of the 20 analyzed examples shows that the value-adding amount of refurbishments is in the range of 34 to 58 percent. The rate tends to be below the rate of cost transfer of 50 to 70 percent according to the VMWG. The developed toolbox provides a decision-making basis to evaluate the value-preserving and the value-adding part. Authors: King, Marvin; Sandmeier, Ernst; Domingo, Silvia.
Abstract For rental properties, the share of value-adding investments in building renovations is of major importance, as these costs may be passed on to the rental. However, the distinction between this and the share of building maintenance covered by the current rent is complex and can be a barrier to such refurbishment projects. Due to the lack of practical instruments, an alternative calculation method “BKP-Triage” was defined together with the clients SFOE & FOH (Federal Office for Housing) and in exchange with partners HEV Schweiz & Tenants' Association. The results of the 20 analyzed examples shows that the value-adding amount of refurbishments is in the range of 34 to 58 percent. The rate tends to be below the rate of cost transfer of 50 to 70 percent according to the VMWG. The developed toolbox provides a decision-making basis to evaluate the value-preserving and the value-adding part. Authors: King, Marvin; Sandmeier, Ernst; Domingo, Silvia.
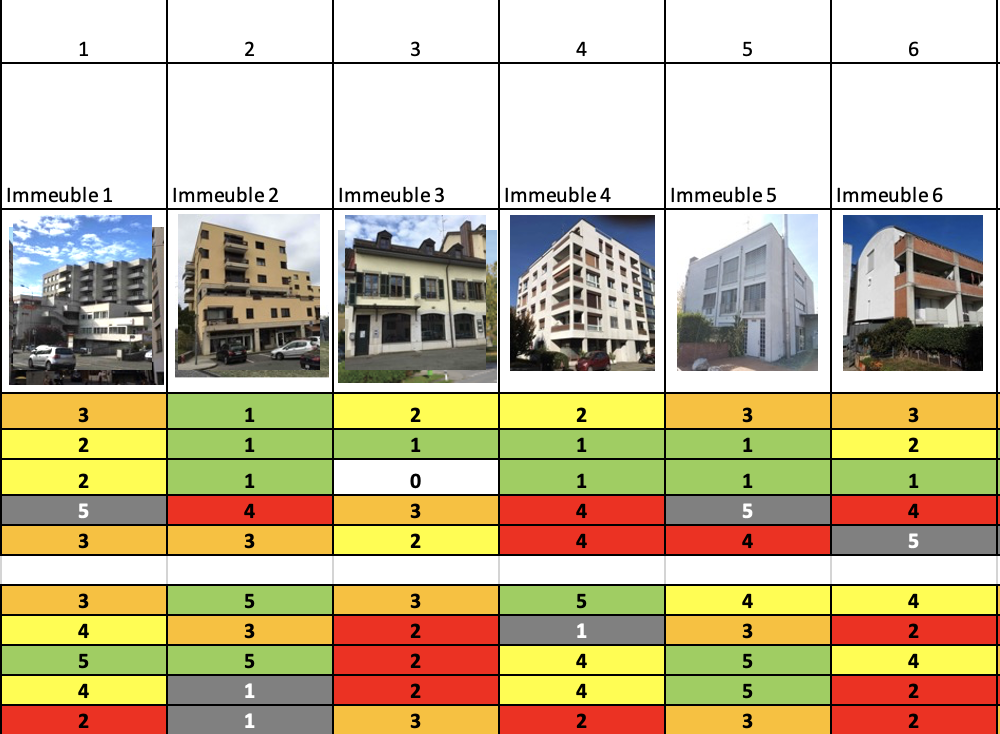
Digital steering tool for real estate portfolio owners
Abstract Owners of buildings constructed during the construction boom of the 1950s to 1980s have a responsibility (and in some cases an obligation) to renovate their property to reduce energy consumption. For certain owners with several buildings in their portfolio, the question of prioritizing renovation work can become a major challenge. The Excel tool developed by HEPIA and made available as part of RENOWAVE enables owners to produce an initial assessment of the order in which the problem should be tackled, and of the cost of each operation. It allows them to do this independently, at a lower cost, without the need to hire an real estate professional or to use portfolio assessment softwares, often too complex and sophisticated to meet this need at first instance. Author: Rinquet, Lionel.
Abstract Owners of buildings constructed during the construction boom of the 1950s to 1980s have a responsibility (and in some cases an obligation) to renovate their property to reduce energy consumption. For certain owners with several buildings in their portfolio, the question of prioritizing renovation work can become a major challenge. The Excel tool developed by HEPIA and made available as part of RENOWAVE enables owners to produce an initial assessment of the order in which the problem should be tackled, and of the cost of each operation. It allows them to do this independently, at a lower cost, without the need to hire an real estate professional or to use portfolio assessment softwares, often too complex and sophisticated to meet this need at first instance. Author: Rinquet, Lionel.
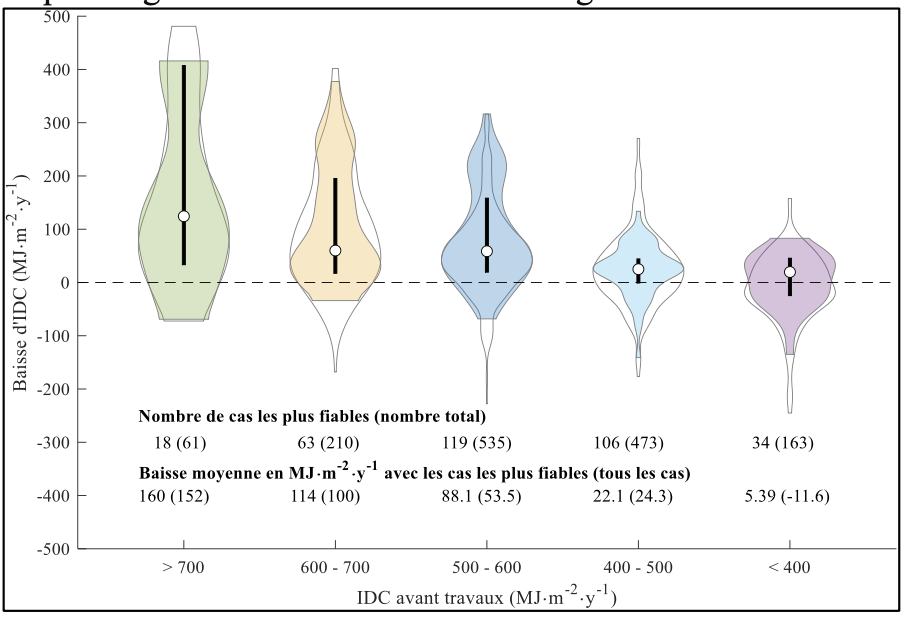
Actual energy savings of more than 1000 renovated buildings in Geneva
Abstract This study quantifies the annual energy-related retrofit rate of the Geneva building stock (1.7%), based on data concerning the delivered construction permits over the 2010 – 2018 period. By cross-cutting with final energy demand before and after retrofit, we derive an energy- efficient retrofit rate (0.6% for an improvement of 1 class at least, 0.2% for 2 classes at least). Results are analysed as a function of the construction period, as well as of the energy demand before retrofit. Authors: Grandjean, Basile; Schneider, Stefan; Hollmuller, Pierre. Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.
Abstract This study quantifies the annual energy-related retrofit rate of the Geneva building stock (1.7%), based on data concerning the delivered construction permits over the 2010 – 2018 period. By cross-cutting with final energy demand before and after retrofit, we derive an energy- efficient retrofit rate (0.6% for an improvement of 1 class at least, 0.2% for 2 classes at least). Results are analysed as a function of the construction period, as well as of the energy demand before retrofit. Authors: Grandjean, Basile; Schneider, Stefan; Hollmuller, Pierre. Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.
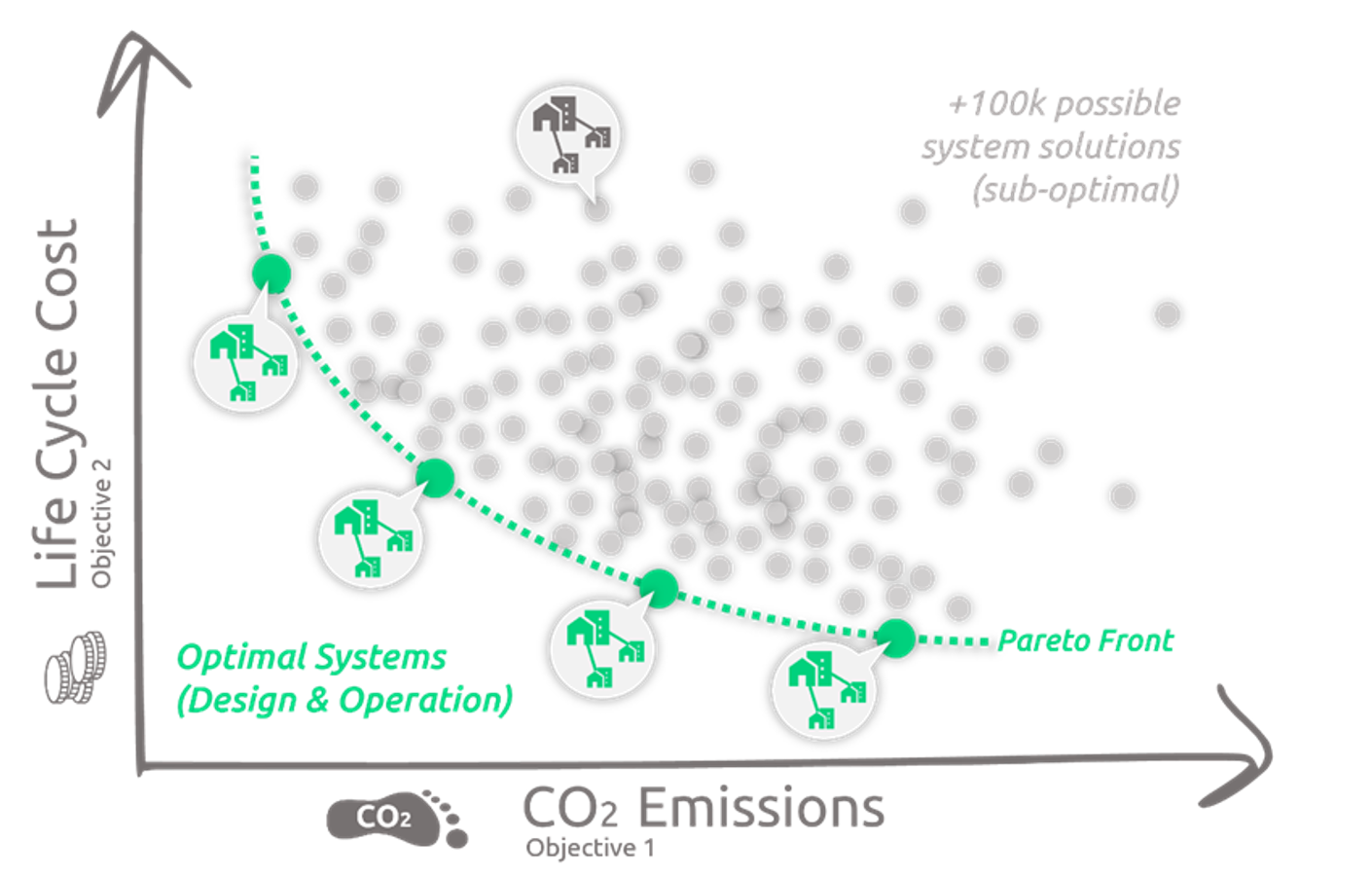
District scale simulation for supporting decarbonising plans
Abstract In energy planning of districts, it is often unclear what energy supply options are available and what influence different technology options have, including demand reduction through energy renovation. Thus, the use of a simulation and optimization tools is explored in the planning process of a specific case study in Switzerland. Four different scenarios were developed and annual life cycle costs (LCC) as well as CO2 emissions, are proposed. The results of the respective scenarios are categorized and compared according to CO2 emissions and LCC. It becomes clear that for CO2 emissions, there is a large reduction potential (up to 90%) with different LCC. Authors: Haase, Matthias.
Abstract In energy planning of districts, it is often unclear what energy supply options are available and what influence different technology options have, including demand reduction through energy renovation. Thus, the use of a simulation and optimization tools is explored in the planning process of a specific case study in Switzerland. Four different scenarios were developed and annual life cycle costs (LCC) as well as CO2 emissions, are proposed. The results of the respective scenarios are categorized and compared according to CO2 emissions and LCC. It becomes clear that for CO2 emissions, there is a large reduction potential (up to 90%) with different LCC. Authors: Haase, Matthias.
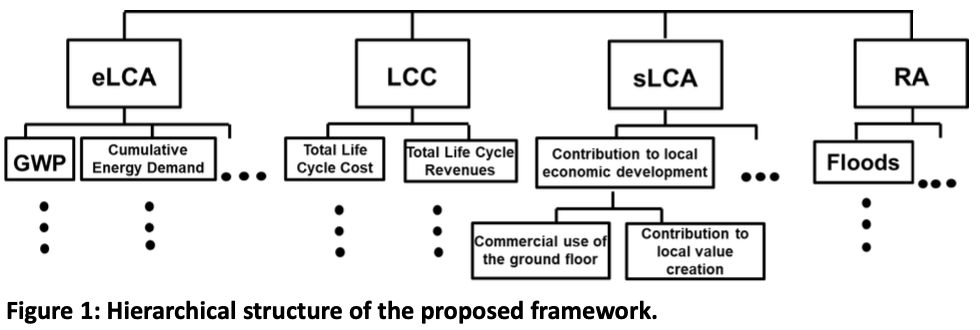
Initial Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment - Aligned general framework characteristics and selected Sustainability Indicators
Abstract To develop a holistic Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment Framework (LCSA-F) for building renovation measures, environmental and social Life Cycle Assessment, Life Cycle Costing and Resilience Assessment were integrated into a Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis. General framework characteristics and sustainability indicators were selected by literature review and stakeholder workshops. Further, the LCSA-F will be tested in case studies to derive the final LCSA-F as a tool to support informed decision-making for the most sustainable measures and the decarbonization of the Swiss building stock. Authors: Baumgartner, Corinna; Spada, Matteo; Lobsiger Kägi, Evelyn.
Abstract To develop a holistic Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment Framework (LCSA-F) for building renovation measures, environmental and social Life Cycle Assessment, Life Cycle Costing and Resilience Assessment were integrated into a Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis. General framework characteristics and sustainability indicators were selected by literature review and stakeholder workshops. Further, the LCSA-F will be tested in case studies to derive the final LCSA-F as a tool to support informed decision-making for the most sustainable measures and the decarbonization of the Swiss building stock. Authors: Baumgartner, Corinna; Spada, Matteo; Lobsiger Kägi, Evelyn.
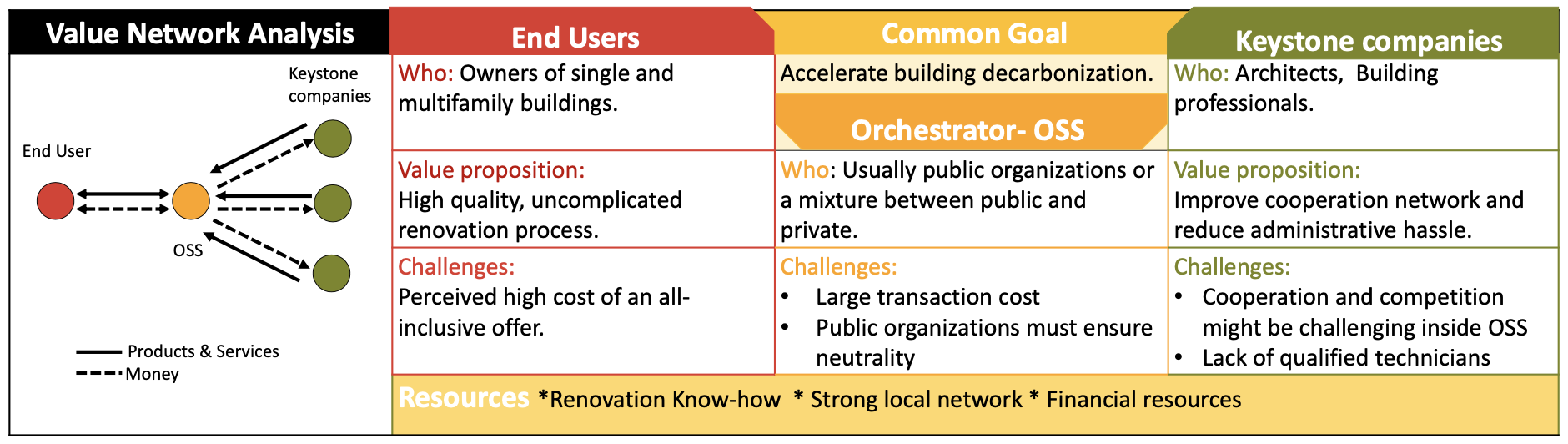
Innovative business model to foster renewable heating and renovation
Abstract Accelerating the building renovation and switching to a renewable heating system are a fundamental part to achieve the CO2 emission reductions goals on time. We have studied several business models such as contracting solutions and one stop shops to find out: which actors play a crucial role? which are their perceived advantages and disadvantages and how can business model innovation help to align their interest towards a competitive business ecosystem? Authors: Zapata, Juliana; Ulli-Beer, Silvia.
Abstract Accelerating the building renovation and switching to a renewable heating system are a fundamental part to achieve the CO2 emission reductions goals on time. We have studied several business models such as contracting solutions and one stop shops to find out: which actors play a crucial role? which are their perceived advantages and disadvantages and how can business model innovation help to align their interest towards a competitive business ecosystem? Authors: Zapata, Juliana; Ulli-Beer, Silvia.
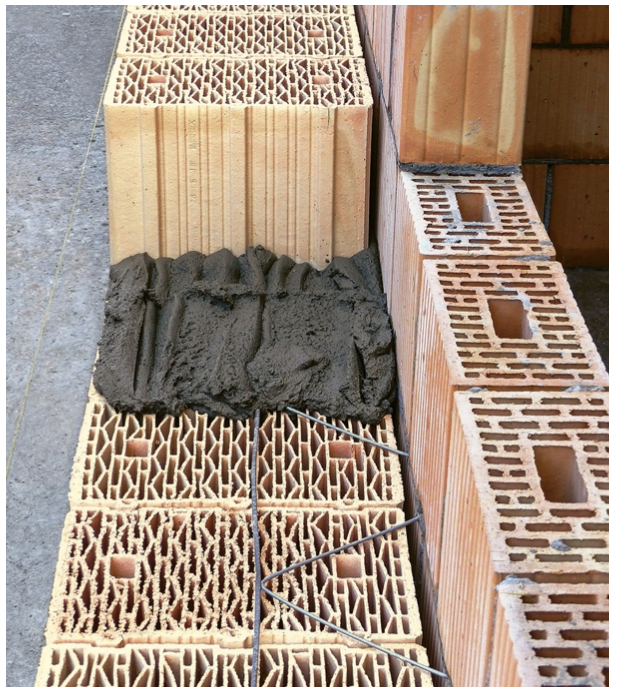

A preview of practical solutions for the use of insulating bricks
Abstract To increase the rate of renewal in the building sector, new renovation strategies and durable measures are needed. The standard thermal insulation composite system (WDVS) is not sustainable in several ways. Building owners and investors are increasingly recognizing the advantages of diffusion-open wall systems and large storage masses such as insulation bricks. In the project, the energetic potential of alternative insulation systems for refurbishment is being holistically analyzed and optimized in terms of the market together with stakeholders. Based on a previous project collaboration with Keller AG Ziegeleien, the KISmur façade system was further developed for refurbishments. The analysis consists of the existing structural layer and an added layer of the developed insulating brick. Authors: Köster, Sandra; King, Marvin.
Abstract To increase the rate of renewal in the building sector, new renovation strategies and durable measures are needed. The standard thermal insulation composite system (WDVS) is not sustainable in several ways. Building owners and investors are increasingly recognizing the advantages of diffusion-open wall systems and large storage masses such as insulation bricks. In the project, the energetic potential of alternative insulation systems for refurbishment is being holistically analyzed and optimized in terms of the market together with stakeholders. Based on a previous project collaboration with Keller AG Ziegeleien, the KISmur façade system was further developed for refurbishments. The analysis consists of the existing structural layer and an added layer of the developed insulating brick. Authors: Köster, Sandra; King, Marvin.
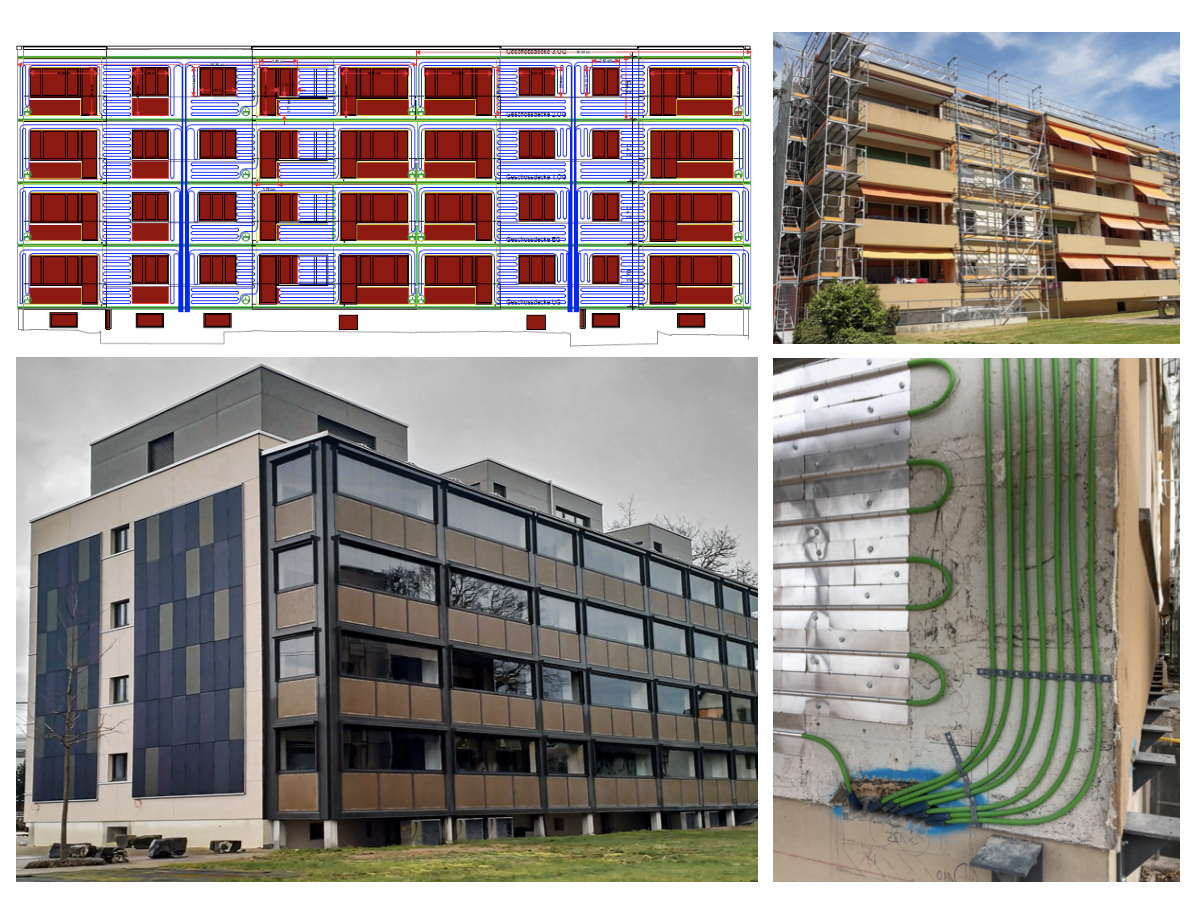

External wall heating system: Renovation of a MFH to nZEB standard
Abstract Thermal insulation, comfort ventilation, low-temperature heat distribution, and thermal component activation: what is usually planned separately and can only be implemented after the inhabitants have moved out, is installed in "ProsumerSkin" in a single step. The system is being tested in a P&D project in Bern on an inhabited building as part of a serial refurbishment using prefabricated façade elements. This simplifies the renovation of uninsulated apartment buildings into net-zero buildings. Authors: Schmitt, Alexander; Philippen, Daniel; Bosshard, Igor.
Abstract Thermal insulation, comfort ventilation, low-temperature heat distribution, and thermal component activation: what is usually planned separately and can only be implemented after the inhabitants have moved out, is installed in "ProsumerSkin" in a single step. The system is being tested in a P&D project in Bern on an inhabited building as part of a serial refurbishment using prefabricated façade elements. This simplifies the renovation of uninsulated apartment buildings into net-zero buildings. Authors: Schmitt, Alexander; Philippen, Daniel; Bosshard, Igor.
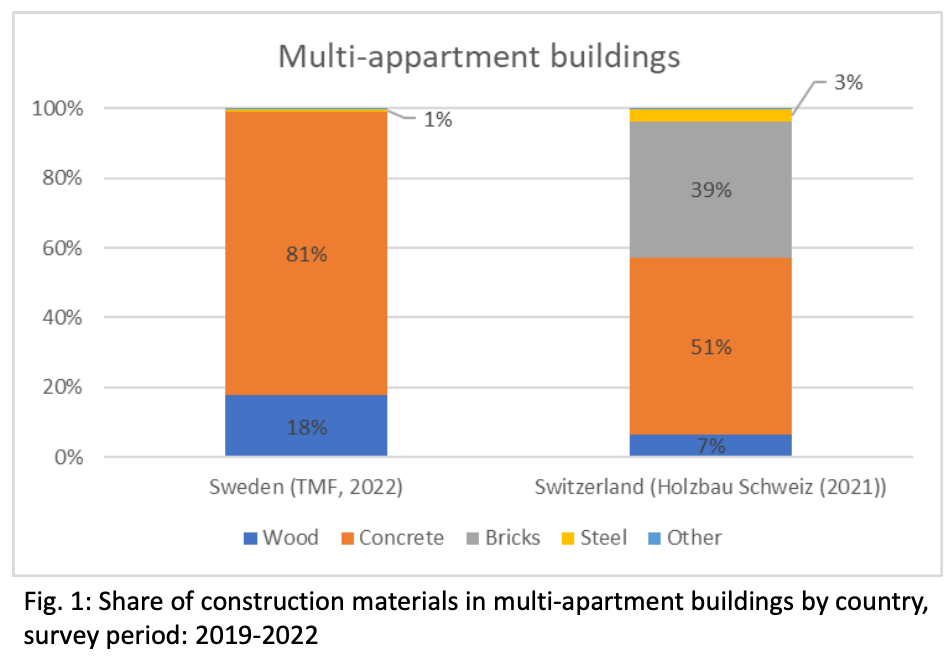
Utilising a system framework in order to identify radical innovations in Swiss building renovation: a research approach and initial findings
Abstract Sustainable, wide-ranging decarbonisation of the Swiss building stock through low-carbon renovation necessitates an efficient interplay of targeted developments in the technological, social and institutional spheres with system-level, sectoral transitions. This is particularly the case for radical innovations, which can take the form of material innovations, including novel uses for existing materials such as wood, as well as process innovations such as the re-use of building materials, as well as support circular economy approaches. In this poster, the authors present the innovation system framework utilized to assess radical innovations in the (Swiss) building sector, as well as initial findings on innovations in the use of wood in renovation drawing on both Swiss and international best practice cases. Authors: Vögeli, Pascal; Sentic, Anton; Markard, Jochen.
Abstract Sustainable, wide-ranging decarbonisation of the Swiss building stock through low-carbon renovation necessitates an efficient interplay of targeted developments in the technological, social and institutional spheres with system-level, sectoral transitions. This is particularly the case for radical innovations, which can take the form of material innovations, including novel uses for existing materials such as wood, as well as process innovations such as the re-use of building materials, as well as support circular economy approaches. In this poster, the authors present the innovation system framework utilized to assess radical innovations in the (Swiss) building sector, as well as initial findings on innovations in the use of wood in renovation drawing on both Swiss and international best practice cases. Authors: Vögeli, Pascal; Sentic, Anton; Markard, Jochen.
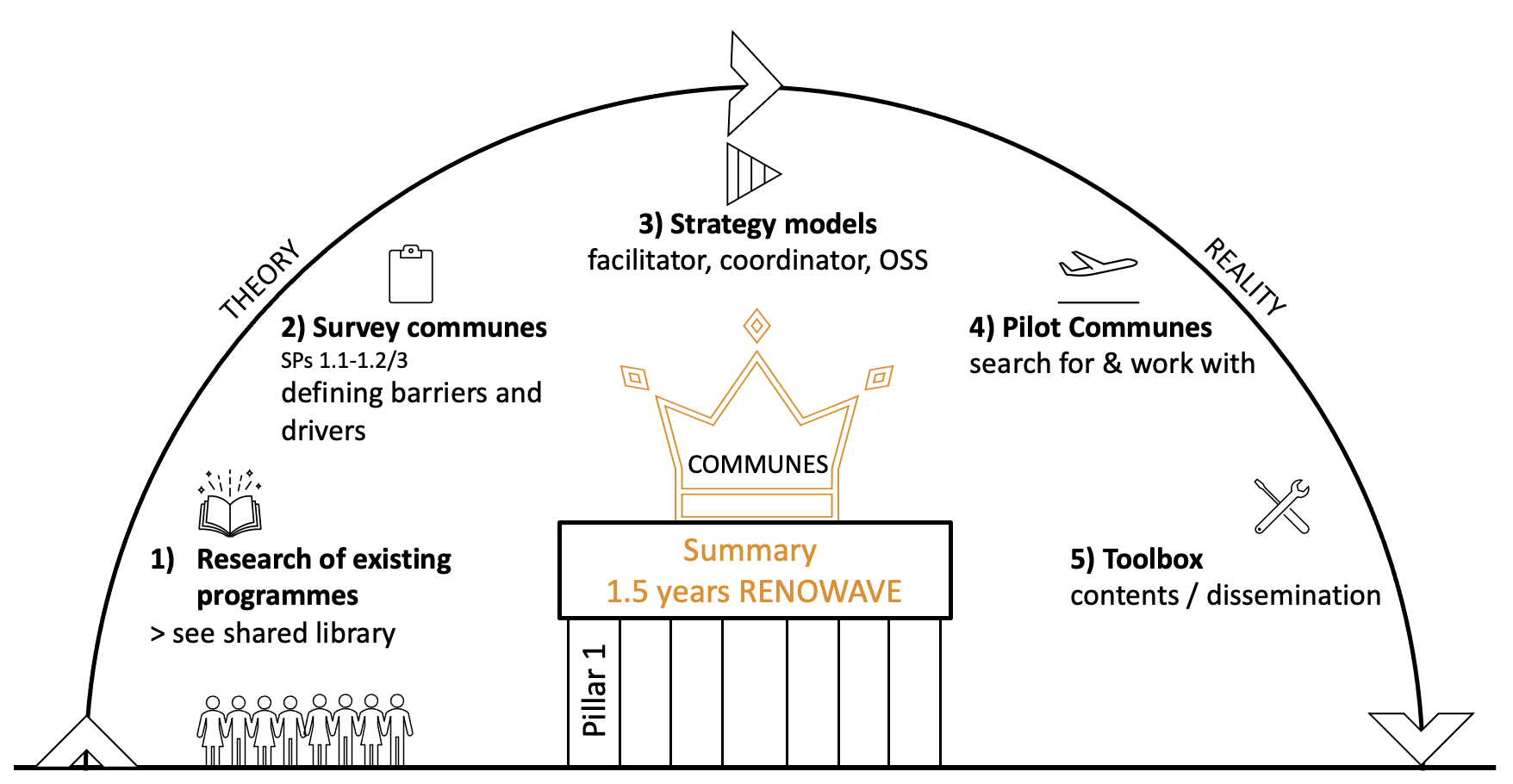
Policy analysis, incentive programs and coaching tools at municipal level : from theory to reality
Abstract Municipalities play a central role in the renovation process of the Swiss building stock. Local authorities are close to the residents and know their territory. They should set the example with their own building stock and support private owners towards ambitious energy renovations. While reducing of energy consumption may seem obvious to most of us, Swiss municipalities are bombarded with numerous action plans in which renovation plays little or no role. Within Renowave, we are identifying barriers and drivers of energy renovation at the municipal level and help municipalities take measures to encourage building owners to renovate. To that end, we are developing, in collaboration with our pilot municipalities, a robust, simple and accessible toolbox, to empower local authorities to support homeowners in their renovation projects. Author: Fowler, Grit.
Abstract Municipalities play a central role in the renovation process of the Swiss building stock. Local authorities are close to the residents and know their territory. They should set the example with their own building stock and support private owners towards ambitious energy renovations. While reducing of energy consumption may seem obvious to most of us, Swiss municipalities are bombarded with numerous action plans in which renovation plays little or no role. Within Renowave, we are identifying barriers and drivers of energy renovation at the municipal level and help municipalities take measures to encourage building owners to renovate. To that end, we are developing, in collaboration with our pilot municipalities, a robust, simple and accessible toolbox, to empower local authorities to support homeowners in their renovation projects. Author: Fowler, Grit.
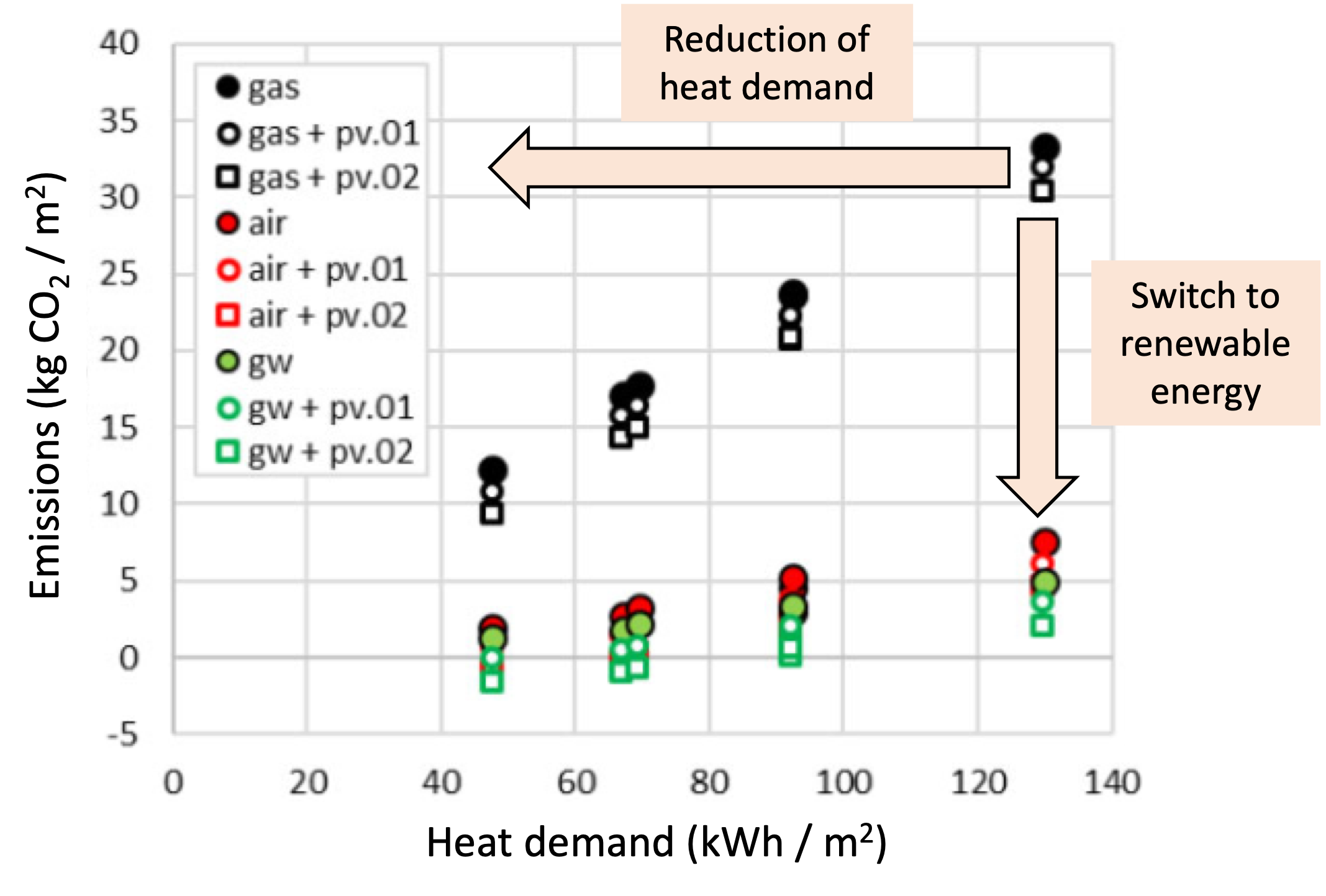
Design and technical improvement of heat-pump systems for existing multifamily buildings
Abstract Switching from fossil boilers to heat pumps (HP) can drastically reduce CO2-emissions of the Swiss building stock. Such can be achieved with or without combined envelope retrofit, which will stretch over several decades. While the potential market is huge, many challenges and obstacles need to be solved, in particular for existing multi-family buildings and related large capacity air-source HPs (> 50 kW). Analysis of case studies in actual condition of use, complemented by numerical simulation, allow to highlight these challenges and indicate potential optimization in terms of sizing, system integration, control strategies, as well as industrial developments. Authors: Hollmuller, Pierre; Montero Dominguez, Omar; Brischoux, Pauline.
Abstract Switching from fossil boilers to heat pumps (HP) can drastically reduce CO2-emissions of the Swiss building stock. Such can be achieved with or without combined envelope retrofit, which will stretch over several decades. While the potential market is huge, many challenges and obstacles need to be solved, in particular for existing multi-family buildings and related large capacity air-source HPs (> 50 kW). Analysis of case studies in actual condition of use, complemented by numerical simulation, allow to highlight these challenges and indicate potential optimization in terms of sizing, system integration, control strategies, as well as industrial developments. Authors: Hollmuller, Pierre; Montero Dominguez, Omar; Brischoux, Pauline.
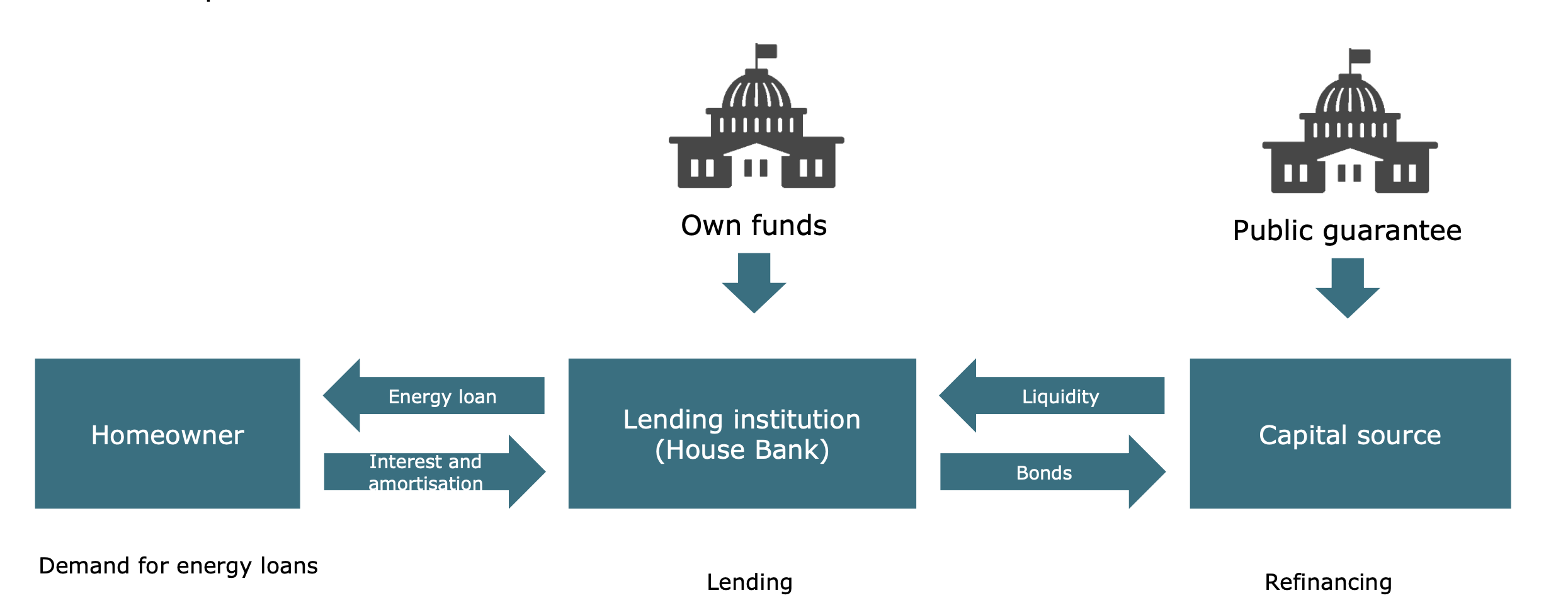
The role of financing in the energy renovation of single-family and private-owned multi-family houses: Recent findings, potential solutions and open questions
Abstract In this project, we investigate the need for complementary financial instruments to accelerate energy retrofits. In particular, we investigate public-private partnership approaches between banks and the public sector, which could be used as a complement to subsidies. A quantitative survey amongst homeowners and interviews with the financial sector have provided first indications regarding the demand for additional financial support and possible solutions. Currently, we are investigating whether further energy retrofits could be initiated by a modification of the banks' lending policy and if so, which regulatory adjustments would be necessary to achieve this. Authors: Gallati, Justus; Drometer, Marcus; Habermacher, Florian et al.
Abstract In this project, we investigate the need for complementary financial instruments to accelerate energy retrofits. In particular, we investigate public-private partnership approaches between banks and the public sector, which could be used as a complement to subsidies. A quantitative survey amongst homeowners and interviews with the financial sector have provided first indications regarding the demand for additional financial support and possible solutions. Currently, we are investigating whether further energy retrofits could be initiated by a modification of the banks' lending policy and if so, which regulatory adjustments would be necessary to achieve this. Authors: Gallati, Justus; Drometer, Marcus; Habermacher, Florian et al.

Building typology - Strategy and roadmap for sustainable renovation
Abstract Which realistic interventions and methodology can help increase the renovation rate of buildings, while guaranteeing quality and durability? The eREN study, conducted by an interdisciplinary team from the HES-SO, has shown that each era has its own architectural and constructional characteristics which must be considered by the energy renovation strategy. The study established representative typologies for 20th century residential buildings, as well as a working tool for the global energy renovation of the envelope. Renovations must be considered as a sustainable optimization process that includes embodied and operational emissions and the time-frame of interventions. The global eREN approach is completed by an environmental assessment, an evaluation of the technical installations and the obsolescence of the construction elements. Finally, a roadmap illustrating necessary works and investments as well as the impacts of stepwise interventions is presented, showing technically and economically viable renovation measures ensuring the achievement of the overall climate targets. Author: Schwab, Stefanie.
Abstract Which realistic interventions and methodology can help increase the renovation rate of buildings, while guaranteeing quality and durability? The eREN study, conducted by an interdisciplinary team from the HES-SO, has shown that each era has its own architectural and constructional characteristics which must be considered by the energy renovation strategy. The study established representative typologies for 20th century residential buildings, as well as a working tool for the global energy renovation of the envelope. Renovations must be considered as a sustainable optimization process that includes embodied and operational emissions and the time-frame of interventions. The global eREN approach is completed by an environmental assessment, an evaluation of the technical installations and the obsolescence of the construction elements. Finally, a roadmap illustrating necessary works and investments as well as the impacts of stepwise interventions is presented, showing technically and economically viable renovation measures ensuring the achievement of the overall climate targets. Author: Schwab, Stefanie.

Renewable heating program: training course, Geneva
Date: 29-01-2024 Time: 13h30-17h30 Location: Chemin du Château-Bloch 2, Vernier, Schweiz Description The aim of this course is to become familiar with SuisseEnergie’s “chauffez renouvelable” program and to help building owners switch to renewable heating systems. Content - Background information on the "chauffez renouvelable" incentive program and advice. - Cantonal legal framework conditions and energy promotion programs in French-speaking Switzerland. - Contents, procedure and tools for incentive advice. - Using the calculation tool and checklist/advice report. - Specific target groups. - Owner-occupied communities and large multi-family homes. - Admission to the list of advisors and promotion of incentive advice. For more information: https://impulsberatung.energie-event.ch/formations_inhouse_pour_entreprises/view/event/12024?elid=235993 Organizer: SIG
Date: 29-01-2024 Time: 13h30-17h30 Location: Chemin du Château-Bloch 2, Vernier, Schweiz Description The aim of this course is to become familiar with SuisseEnergie’s “chauffez renouvelable” program and to help building owners switch to renewable heating systems. Content - Background information on the "chauffez renouvelable" incentive program and advice. - Cantonal legal framework conditions and energy promotion programs in French-speaking Switzerland. - Contents, procedure and tools for incentive advice. - Using the calculation tool and checklist/advice report. - Specific target groups. - Owner-occupied communities and large multi-family homes. - Admission to the list of advisors and promotion of incentive advice. For more information: https://impulsberatung.energie-event.ch/formations_inhouse_pour_entreprises/view/event/12024?elid=235993 Organizer: SIG
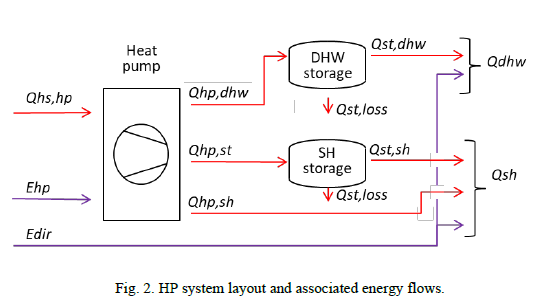
CO2 emission savings of heat-pumps in the residential sector. Case study for multifamily buildings in Geneva
Abstract The present paper assesses the CO2 emissions of air-source and groundwater-source HP systems, with and without complementary PV, for a sample of multifamily buildings (new, retrofitted and non-retrofitted) located in Geneva. HP performance is evaluated by way of numerical simulation in hourly time step, and is cross-cut with the hourly grid CO2 content of the Swiss electricity mix (taking into account both domestic generation and imports from the neighbor countries). Given the seasonal trend of both the building heat demand and the grid CO2 content, latter turns out to strongly underestimate the CO2 content of the HP system electricity. Nonetheless, when compared with a gas boiler, both HP systems induce important annual CO2 savings (air: 61 - 81% depending on the accounting method; groundwater: 75% - 87%). Finally, while PV can substantially contribute to the summer HP demand, the related annual CO2 savings remain relatively marginal, also due to seasonality of the grid CO2 content. Authors: Romano, Elliot; De Sousa Fraga, Carolina; Hollmuller, Pierre. Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.
Abstract The present paper assesses the CO2 emissions of air-source and groundwater-source HP systems, with and without complementary PV, for a sample of multifamily buildings (new, retrofitted and non-retrofitted) located in Geneva. HP performance is evaluated by way of numerical simulation in hourly time step, and is cross-cut with the hourly grid CO2 content of the Swiss electricity mix (taking into account both domestic generation and imports from the neighbor countries). Given the seasonal trend of both the building heat demand and the grid CO2 content, latter turns out to strongly underestimate the CO2 content of the HP system electricity. Nonetheless, when compared with a gas boiler, both HP systems induce important annual CO2 savings (air: 61 - 81% depending on the accounting method; groundwater: 75% - 87%). Finally, while PV can substantially contribute to the summer HP demand, the related annual CO2 savings remain relatively marginal, also due to seasonality of the grid CO2 content. Authors: Romano, Elliot; De Sousa Fraga, Carolina; Hollmuller, Pierre. Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.
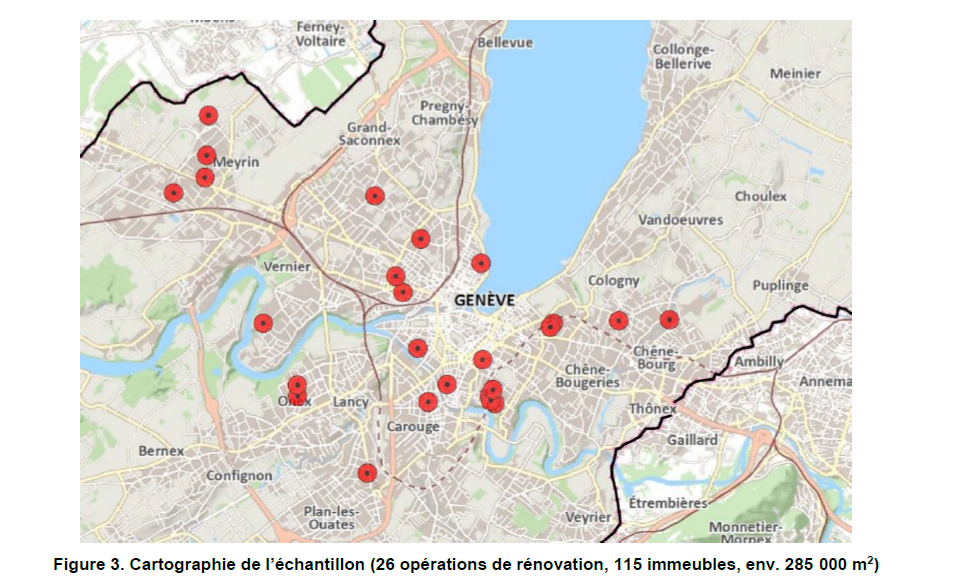
COMPARE RENOVE: energy retrofit of multifamily buildings, from a catalog of solutions to actual performance of energy retrofit
Abstract This study focuses on energy retrofit of post-war multifamily residential buildings, in view of characterizing and improving of current practices. The first part concerns the energy, economic and environmental assessment of 26 retrofit operations, totalizing 3’000 flats and 285’000 m2 heated area. The space heating demand in real conditions of use is compared to the project value, calculated in standard conditions of use. The performance gap is analyzed by way of numeric simulation. At economic level, the retrofit operations are analyzed in terms of costs with energy added value. As a complement, the second part of the study concern specific energy efficiency solutions, which are analyzed on the basis of cases studies operated in real condition of use. The first solution concerns closing of existing balconies in the form of loggias. The second solution concerns heat recovery on exhaust air for preheating of domestic hot water, by way of a heat pump. We finally elaborate recommendations and guidelines for the pre-design of such systems. Full report: https://archive-ouverte.unige.ch/unige:101940 Authors: Khoury, Jad; Hollmuller, Pierre; Lachal, Bernard Marie; Schneider, Stefan; Lehmann, Ursula. Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.
Abstract This study focuses on energy retrofit of post-war multifamily residential buildings, in view of characterizing and improving of current practices. The first part concerns the energy, economic and environmental assessment of 26 retrofit operations, totalizing 3’000 flats and 285’000 m2 heated area. The space heating demand in real conditions of use is compared to the project value, calculated in standard conditions of use. The performance gap is analyzed by way of numeric simulation. At economic level, the retrofit operations are analyzed in terms of costs with energy added value. As a complement, the second part of the study concern specific energy efficiency solutions, which are analyzed on the basis of cases studies operated in real condition of use. The first solution concerns closing of existing balconies in the form of loggias. The second solution concerns heat recovery on exhaust air for preheating of domestic hot water, by way of a heat pump. We finally elaborate recommendations and guidelines for the pre-design of such systems. Full report: https://archive-ouverte.unige.ch/unige:101940 Authors: Khoury, Jad; Hollmuller, Pierre; Lachal, Bernard Marie; Schneider, Stefan; Lehmann, Ursula. Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.
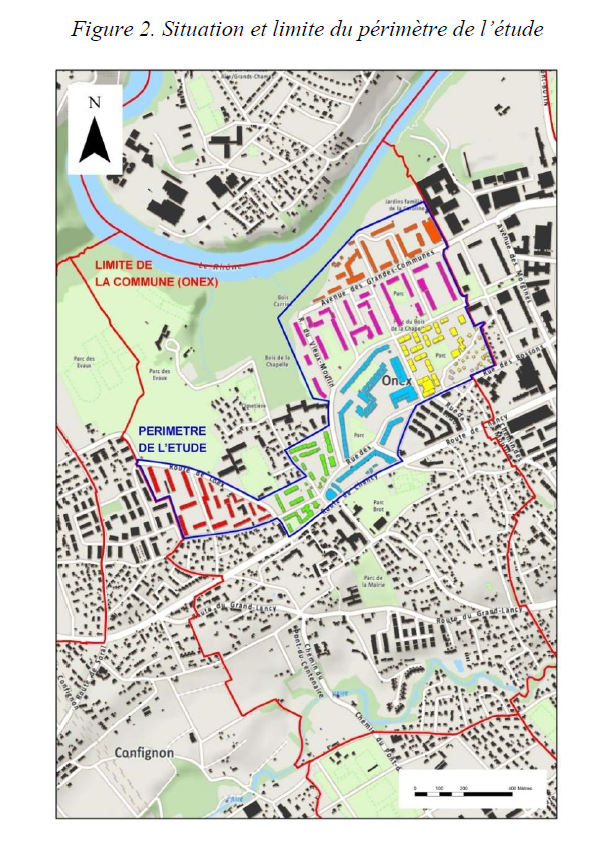
Onex Renove: Typological and energy analysis of multifamily buildings in an urban suburb of Geneva
Abstract Built in the 60's -70's, the new City Onex is about 600'000 m2 of residential buildings with an annual heat consumption of 80 GWh. Aware of the urgent need to increase the energy efficiency in these buildings, the City of Onex and the State of Geneva have recently decided to launch a pilot project, entitled « Onex Renove », that aims to facilitate the participation of building owners and managers in a large-scale energy renovation program. A five-step approach was developed in collaboration with private and public partners, providing building owners involved in this process project support as well as facilitated administrative procedure for renovation. In this context, the main purpose of this study is to provide methodological support for this project, including a building typology study and an overview of the energy consumption of the Onex building stock. The results can be used to better analyze optimized building retrofit strategies per family. The study concludes with a discussion regarding the impact of massive energy renovation of the Onex buildings on the mix heat delivered after the connection of the two main district heating networks CADIOM and CADSIG in Geneva. Authors: Khoury, Jad; Lachal, Bernard Marie; Hollmuller, Pierre. Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.
Abstract Built in the 60's -70's, the new City Onex is about 600'000 m2 of residential buildings with an annual heat consumption of 80 GWh. Aware of the urgent need to increase the energy efficiency in these buildings, the City of Onex and the State of Geneva have recently decided to launch a pilot project, entitled « Onex Renove », that aims to facilitate the participation of building owners and managers in a large-scale energy renovation program. A five-step approach was developed in collaboration with private and public partners, providing building owners involved in this process project support as well as facilitated administrative procedure for renovation. In this context, the main purpose of this study is to provide methodological support for this project, including a building typology study and an overview of the energy consumption of the Onex building stock. The results can be used to better analyze optimized building retrofit strategies per family. The study concludes with a discussion regarding the impact of massive energy renovation of the Onex buildings on the mix heat delivered after the connection of the two main district heating networks CADIOM and CADSIG in Geneva. Authors: Khoury, Jad; Lachal, Bernard Marie; Hollmuller, Pierre. Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.
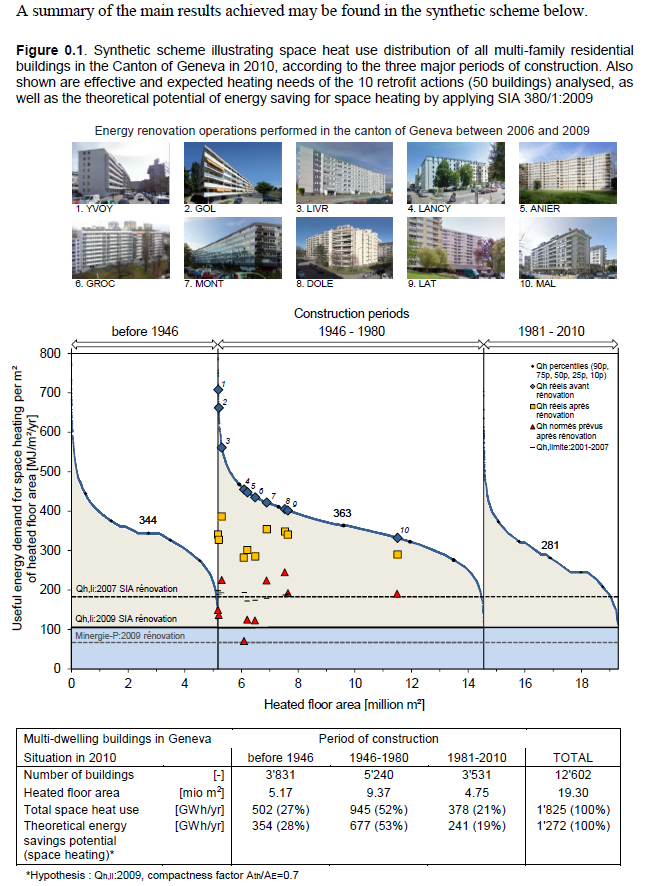
Energy retrofit of multifamily residential buildings: status, case studies and potential for Geneva
Abstract This study focuses on energy retrofitting of multi-family residential buildings in Geneva, integrating technical, economical, financial and environmental aspects, as well as preservation of cultural heritage. The first part of this study shows that multi-family residential buildings in Geneva are responsible for almost half of the thermal energy consumption of the canton as well as half of the CO2 emissions of all the building stock. About half of this consumption and these emissions are caused by post-war multi-family dwellings built between 1946 and 1980, which are nowadays in need of retrofit. The analysis of retrofit dynamics registered between 2004 and 2012 shows a significant increase in energy retrofitting of residential buildings since 2010. The second part of this study deals with the real performance of retrofit actions, with a focus on energy and economic aspects. The study is based on a monitoring campaign implemented in a multi-family building built in 1963 in Onex (GE) that was retrofitted according to the Minergie standard in 2008 and a benchmark study over 10 buildings retrofitted between 2006 and 2009. The assessment of the energy performance of these actions shows that the real space heating demand of the retrofitted buildings is 43% to 142% higher than the expected calculated value. The economic analysis shows that, for achieving the Minergie standard of the post-war multifamily building stock, the global retrofit cost (energy and non-energy related) would be around 10 billion CHF. The last part of this study evaluates the theoretical energy saving potential for space heating in Geneva’s multifamily building stock and provides concrete recommendations to mobilize efficiently this potential. The main conclusion is that the achievement of the ambitious goals set by the federal government is hardly possible without an improvement of the current practices regarding the actors involved in building retrofit process. Author: Khoury, Jad. Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.
Abstract This study focuses on energy retrofitting of multi-family residential buildings in Geneva, integrating technical, economical, financial and environmental aspects, as well as preservation of cultural heritage. The first part of this study shows that multi-family residential buildings in Geneva are responsible for almost half of the thermal energy consumption of the canton as well as half of the CO2 emissions of all the building stock. About half of this consumption and these emissions are caused by post-war multi-family dwellings built between 1946 and 1980, which are nowadays in need of retrofit. The analysis of retrofit dynamics registered between 2004 and 2012 shows a significant increase in energy retrofitting of residential buildings since 2010. The second part of this study deals with the real performance of retrofit actions, with a focus on energy and economic aspects. The study is based on a monitoring campaign implemented in a multi-family building built in 1963 in Onex (GE) that was retrofitted according to the Minergie standard in 2008 and a benchmark study over 10 buildings retrofitted between 2006 and 2009. The assessment of the energy performance of these actions shows that the real space heating demand of the retrofitted buildings is 43% to 142% higher than the expected calculated value. The economic analysis shows that, for achieving the Minergie standard of the post-war multifamily building stock, the global retrofit cost (energy and non-energy related) would be around 10 billion CHF. The last part of this study evaluates the theoretical energy saving potential for space heating in Geneva’s multifamily building stock and provides concrete recommendations to mobilize efficiently this potential. The main conclusion is that the achievement of the ambitious goals set by the federal government is hardly possible without an improvement of the current practices regarding the actors involved in building retrofit process. Author: Khoury, Jad. Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.
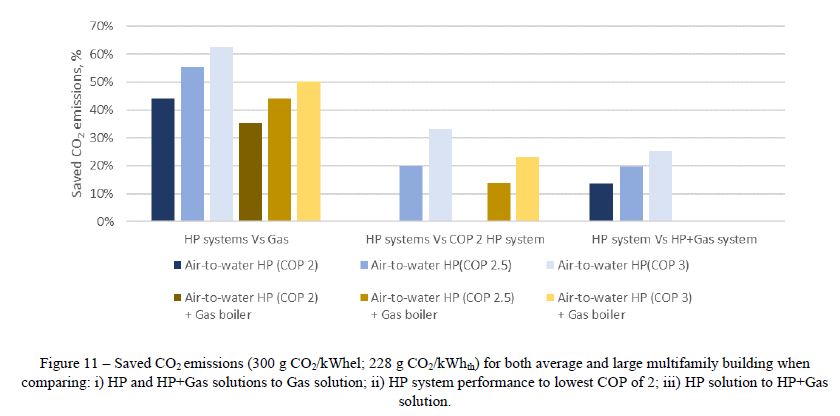
Which performance indicators should we provide to policy makers to switch from gas boilers to air to water heat pumps?
Abstract The most commonly used performance indicator (PI) of heat pump (HP) systems is the COP. But is it a good PI? If so, does it have a minimum threshold? This article covers the potentials and constraints of different PIs for HP systems implemented in non-renovated residential buildings from an environmental, economic and social acceptability point of view, based on real case studies situated in Geneva, Switzerland. After describing the Geneva context and listing the most common PIs, we first compare a traditional gas boiler to an air to water HP system for space heating and domestic hot water of single-family building (SFB). We then follow by a similar comparison for multifamily buildings (MFB). For this particular building demand, a hybrid system is also analyzed (HP combined with gas for the peak loads) and specific PIs are included. Finally, the most pertinent PIs for air to water HP systems are identified and the minimum COP value of 2.5 is recommended to insure the reliability of the system in the 3 mentioned fields in the swiss context. Authors: De Sousa Fraga, Carolina et al. Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.
Abstract The most commonly used performance indicator (PI) of heat pump (HP) systems is the COP. But is it a good PI? If so, does it have a minimum threshold? This article covers the potentials and constraints of different PIs for HP systems implemented in non-renovated residential buildings from an environmental, economic and social acceptability point of view, based on real case studies situated in Geneva, Switzerland. After describing the Geneva context and listing the most common PIs, we first compare a traditional gas boiler to an air to water HP system for space heating and domestic hot water of single-family building (SFB). We then follow by a similar comparison for multifamily buildings (MFB). For this particular building demand, a hybrid system is also analyzed (HP combined with gas for the peak loads) and specific PIs are included. Finally, the most pertinent PIs for air to water HP systems are identified and the minimum COP value of 2.5 is recommended to insure the reliability of the system in the 3 mentioned fields in the swiss context. Authors: De Sousa Fraga, Carolina et al. Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.
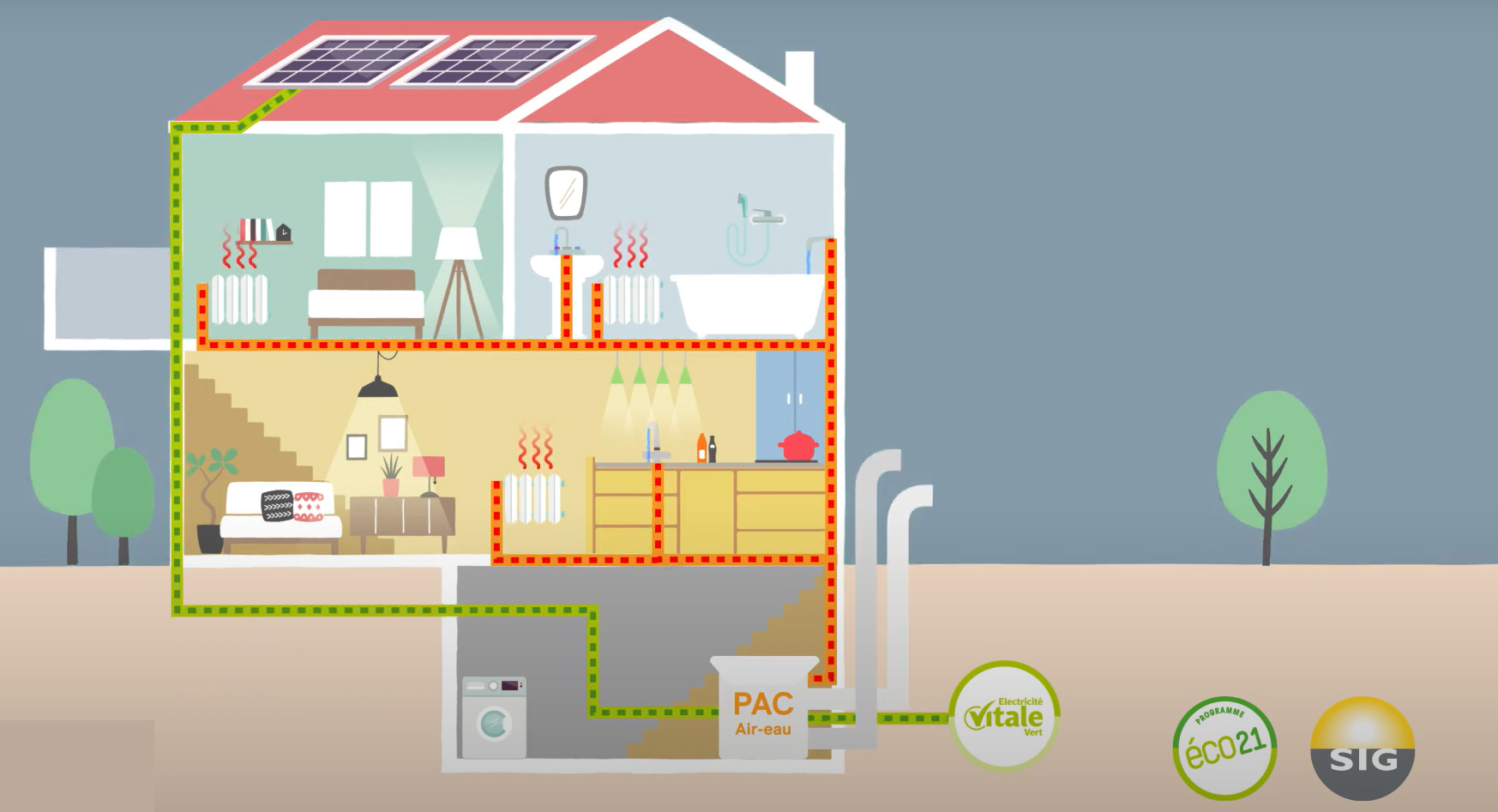
SOS PAC: Monitoring and Optimization of HP Systems
Abstract "Suivi et Optimisation des Systèmes PAC (SOS PAC)" is a special group where engineers and heat technicians share their experience in the monitoring and optimization of large capacity air-to-water heat pump systems used for space heating and domestic hot water production. It is an activity organized by SIG-éco21 and it is solely focused on existing HP systems, located in Geneva. The participants of this group are i) engineers in charge of the optimization of their HP concepts; ii) heat technicians in charge of the optimization and maintenance of HP systems. By exchanging their experiences, the participants can share their good practices as well as benefit from the group’s collective intelligence in the resolution of blocking points in the optimization. To promote transparency and trust, all participants sign a NDA. UNIGE is currently working on a quantitative and qualitative summary, for dissemination of (anonymously) quantitative technical and economic indicators, as well as qualitative aspects concerning the strong and weak points and lessons learned in the various projects. Author: De Sousa Fraga, Carolina.
Abstract "Suivi et Optimisation des Systèmes PAC (SOS PAC)" is a special group where engineers and heat technicians share their experience in the monitoring and optimization of large capacity air-to-water heat pump systems used for space heating and domestic hot water production. It is an activity organized by SIG-éco21 and it is solely focused on existing HP systems, located in Geneva. The participants of this group are i) engineers in charge of the optimization of their HP concepts; ii) heat technicians in charge of the optimization and maintenance of HP systems. By exchanging their experiences, the participants can share their good practices as well as benefit from the group’s collective intelligence in the resolution of blocking points in the optimization. To promote transparency and trust, all participants sign a NDA. UNIGE is currently working on a quantitative and qualitative summary, for dissemination of (anonymously) quantitative technical and economic indicators, as well as qualitative aspects concerning the strong and weak points and lessons learned in the various projects. Author: De Sousa Fraga, Carolina.
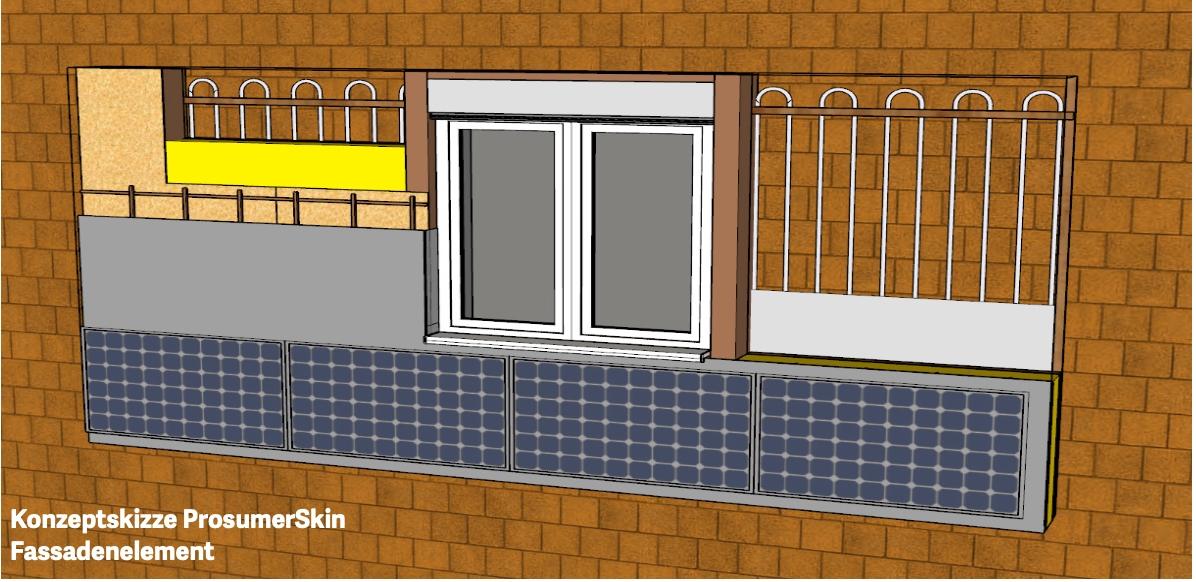
ProsumerSkin
Abstract ProsumerSkin is a new modular and prefabricated façade element for the renovation of badly insulated buildings, developed by our team. The ProsumerSkin can combine several functionalities in one façade element including thermal insulation, new windows, decentralised ventilation with heat-recovery, wall heating replacing radiators inside the building, and building integrated photovoltaics. The high degree of prefabrication increases installation speed and decreases disturbance of occupants, the insulating skin reduces energy demand for space heating to low energy levels, and active energy harvesting and/or energy distributing elements, that are modular add-ons, optimise energy harvesting and distribution according to the specific needs of the building or costumer. Author: Bosshard, Igor.
Abstract ProsumerSkin is a new modular and prefabricated façade element for the renovation of badly insulated buildings, developed by our team. The ProsumerSkin can combine several functionalities in one façade element including thermal insulation, new windows, decentralised ventilation with heat-recovery, wall heating replacing radiators inside the building, and building integrated photovoltaics. The high degree of prefabrication increases installation speed and decreases disturbance of occupants, the insulating skin reduces energy demand for space heating to low energy levels, and active energy harvesting and/or energy distributing elements, that are modular add-ons, optimise energy harvesting and distribution according to the specific needs of the building or costumer. Author: Bosshard, Igor.

Conference on Energy and sustainability law, Winterthur
Date: 30-08-2024 Time: 13h00-17h30 Location: Auditorium, Volkart building, Winterthur, Schweiz The event is open to the public. Registrations will be accepted until August 26, 2024. Description Switzerland's secure and sustainable energy supply has become an issue for the future. The Energy Strategy 2050 provides for the increased use of renewable energy, a reduction in energy consumption and decarbonization. However, the expansion of domestic production leads to conflicts of interest with other, primarily ecological, concerns. The Institute for Regulation and Competition's conference series on energy and sustainability law addresses current issues in an interdisciplinary manner and promotes networking and holistic considerations. Content - Regulation in energy law - Claims, politics and regulation (or: why everything is so complicated ?) - Technical and economic limits of regulation - The limits of private regulation using the example of energy building retrofit - State incentive regulation and its limits using the example of energy communities - Panel discussion: What to do after the vote on the shell decree? For more information and registration: www.zhaw.ch/irw/tagung-ennr Organizers: ZHAW School of Management and Law in cooperation with Renowave and Sweet (Swiss energy research for the energy transition).
Date: 30-08-2024 Time: 13h00-17h30 Location: Auditorium, Volkart building, Winterthur, Schweiz The event is open to the public. Registrations will be accepted until August 26, 2024. Description Switzerland's secure and sustainable energy supply has become an issue for the future. The Energy Strategy 2050 provides for the increased use of renewable energy, a reduction in energy consumption and decarbonization. However, the expansion of domestic production leads to conflicts of interest with other, primarily ecological, concerns. The Institute for Regulation and Competition's conference series on energy and sustainability law addresses current issues in an interdisciplinary manner and promotes networking and holistic considerations. Content - Regulation in energy law - Claims, politics and regulation (or: why everything is so complicated ?) - Technical and economic limits of regulation - The limits of private regulation using the example of energy building retrofit - State incentive regulation and its limits using the example of energy communities - Panel discussion: What to do after the vote on the shell decree? For more information and registration: www.zhaw.ch/irw/tagung-ennr Organizers: ZHAW School of Management and Law in cooperation with Renowave and Sweet (Swiss energy research for the energy transition).

Swiss Green Economy Symposium
Date: 27/29-08-2024 Time: 7h15-18h30 (view full program for more details) Location: Town Hall ZHAW, Winterthur, Switzerland Description The Swiss Green Economy Symposium is the most comprehensive conference on economy and sustainability in Switzerland since 2013. Content - SGEX business field trips - Biodiversity: Understanding conflicts and finding solutions together - Advancing the circular economy: batteries and other sectors - Sustainable supply chains: Overcoming risks together - Innovation forums - Implementing the circular economy - Building and living: sustainable and healthy - Solving conflicts together using climate protection as an example - Carbon Capture: How do we create an effective ecosystem? - Award ceremonies - Cultural evening For more information: https://sges.ch/ For ticketing: https://lifefair.libracore.ch/tickets?anlass=SGES%202024&source=sges Organizer: SGES.
Date: 27/29-08-2024 Time: 7h15-18h30 (view full program for more details) Location: Town Hall ZHAW, Winterthur, Switzerland Description The Swiss Green Economy Symposium is the most comprehensive conference on economy and sustainability in Switzerland since 2013. Content - SGEX business field trips - Biodiversity: Understanding conflicts and finding solutions together - Advancing the circular economy: batteries and other sectors - Sustainable supply chains: Overcoming risks together - Innovation forums - Implementing the circular economy - Building and living: sustainable and healthy - Solving conflicts together using climate protection as an example - Carbon Capture: How do we create an effective ecosystem? - Award ceremonies - Cultural evening For more information: https://sges.ch/ For ticketing: https://lifefair.libracore.ch/tickets?anlass=SGES%202024&source=sges Organizer: SGES.
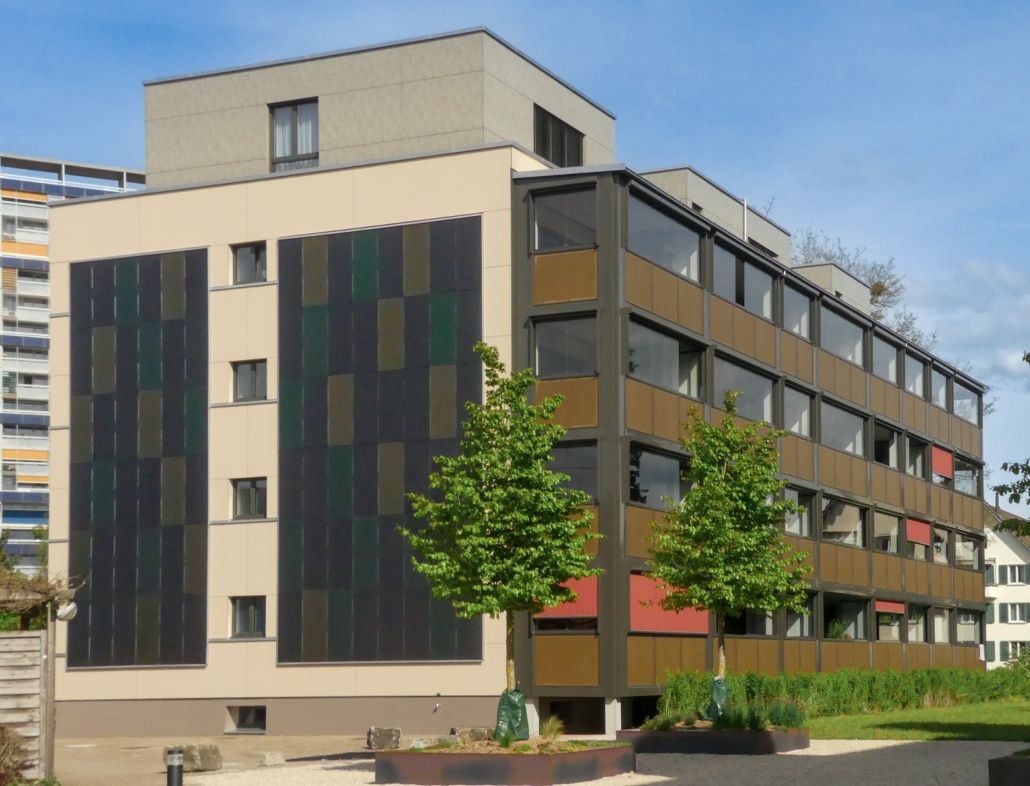

Infoblatt zur aussenliegende Wandheizung
Abstract Das Infoblatt zeigt auf zwei Seiten übersichtlich die Funktionen der aussenliegenden Wandheizung und die Vorteile für Bauherrschaft und Bewohnende auf. Author: Philippen, Daniel (OST).
Abstract Das Infoblatt zeigt auf zwei Seiten übersichtlich die Funktionen der aussenliegenden Wandheizung und die Vorteile für Bauherrschaft und Bewohnende auf. Author: Philippen, Daniel (OST).
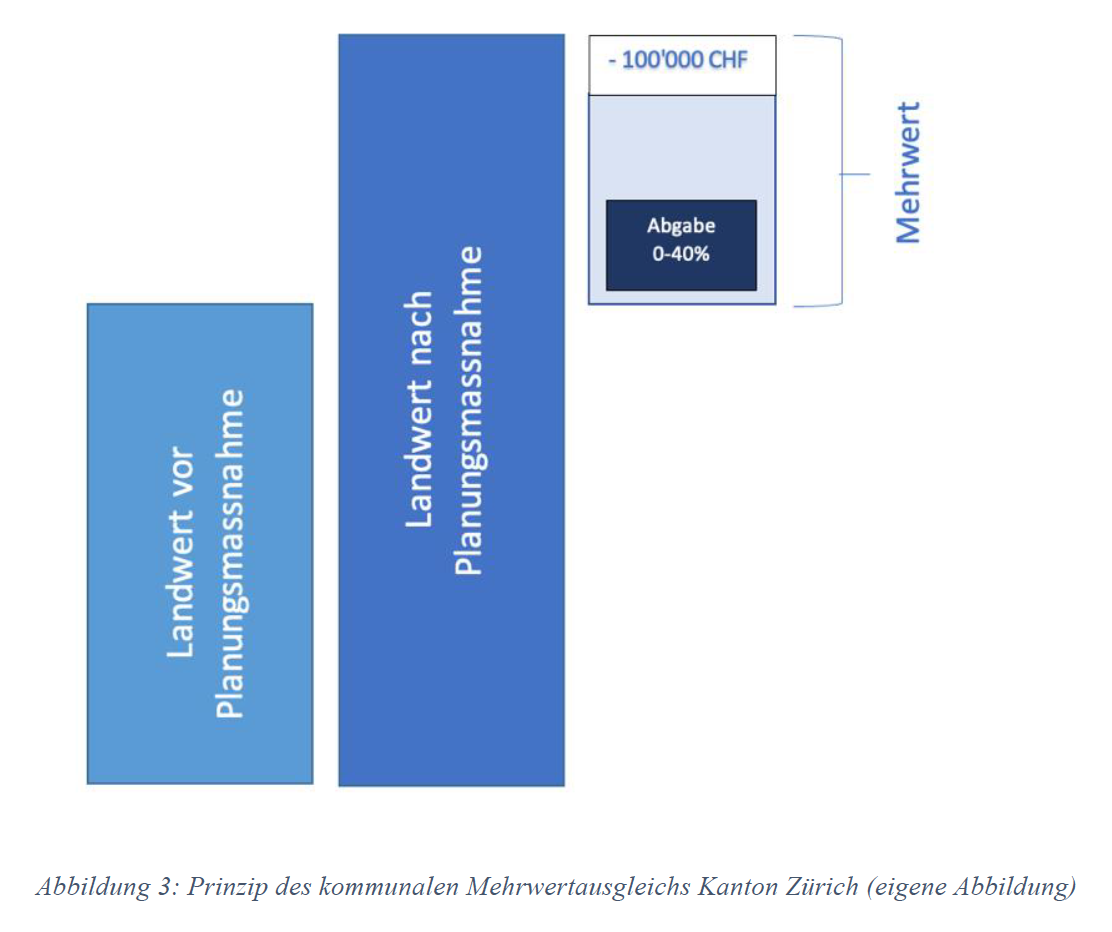
Der Mehrwertausgleich und seine möglichen Folgen für eine nachhaltige Immobilienentwicklung
Abstract Vor dem Hintergrund der übergeordneten Ziele der Raumplanung müssen Bund, Kantone und Gemeinden in der Schweiz den Boden haushälterisch nutzen und Baugebiet von Nichtbaugebiet trennen. Dabei steht die Siedlungsentwicklung nach innen sowie die Verdichtung im Vordergrund. Der Mehrwertausgleich soll als wichtiges Instrument dienen, um der Zersiedelung entgegenzuwirken und die angestrebte Verdichtung zu unterstützen. Der Mehrwertausgleich gemäss Art. 5 RPG verlangt von den Kantonen, bedeutende Vorteile durch planungsbedingte Mehrwerte teilweise abzuschöpfen. Planungsbedingte Bodenwertsteigerungen gelten dabei als planungsbedingte Vorteile. Die Realisierung einer inneren Verdichtung ist allerdings nur möglich, wenn Grundstückseigentümer*innen und Investor*innen bereit sind, Verdichtungsprojekte umzusetzen. Insgesamt müssen bei der Umsetzung von solchen Projekten eine Vielzahl von Faktoren berücksichtigt werden, darunter die wirtschaftliche Rentabilität, die Auswirkungen auf den Immobilienmarkt sowie die Boden- und Mietpreisentwicklung. Einerseits kann die Mehrwertabgabe das Potential für eine grössere Nutzungsdichte verringern, da die Abgabe möglicherweise Anreize zur Reduzierung der Bauaktivität und damit zu einer geringeren Ausnutzung des Potenzials für eine verdichtete Entwicklung schafft, andererseits entsteht aufgrund der zahlreichen Projektrisiken eine gewisse Planungsunsicherheit. Diese Unsicherheit kann dazu führen, dass Investierende zögern, Verdichtungsprojekte zu initiieren. Die vorliegende Arbeit untersucht die Umsetzung der kommunalen Mehrwertabgabe und deren Auswirkungen auf Immobilienentwicklungen in den Gemeinden des Kantons Zürich. Dabei werden die Auswirkungen auf raumplanerische Ziele, Boden- und Mietpreise sowie die Immobilienbranche behandelt. Anhand von zwei Fallbeispielen wird mithilfe der DCF-Methode geprüft, inwiefern die Mehrwertabgabe die Wirtschaftlichkeit von verschiedenen Projektvarianten beeinflusst. Des Weiteren wird durch die Ergebnisse der Berechnungen ermittelt, ob der Mehrwertausgleich einen Anreiz für Sanierungen ohne Erweiterung und gegen Neubauten mit erhöhter Ausnützung setzt. Ausserdem wird aufgezeigt, ob durch die Mehrwertabgabe ein Anreiz gegen eine Verdichtung erfolgt. Mit der letzten Forschungsfrage wird geklärt, wie nachhaltig die finanziellen Mittel schlussendlich mittels Mehrwertausgleichsfonds eingesetzt werden. Abschliessend kann festgestellt werden, dass Ersatzneubauten mit erhöhter Ausnützung trotz der Mehrwertabgabe für Grundstückbesitzende wirtschaftlich attraktiv sind. Die Mehrwertabgabe stellt, unter der Voraussetzung einer gleichbleibenden Konjunktur kein Hindernis für eine Verdichtung dar. Wie nachhaltig die finanziellen Mittel schlussendlich eingesetzt werden, kann nicht abschliessend beurteilt werden, da noch nicht genügend Mittel verfügbar sind. Eine ganzheitliche Betrachtung der wirtschaftlichen Rentabilität, deren Auswirkungen auf den Immobilienmarkt sowie die Boden- und Mietpreisentwicklung ist erforderlich, um die Umsetzung von Verdichtungsprojekten zu unterstützen. Author: Siegl Jan Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.
Abstract Vor dem Hintergrund der übergeordneten Ziele der Raumplanung müssen Bund, Kantone und Gemeinden in der Schweiz den Boden haushälterisch nutzen und Baugebiet von Nichtbaugebiet trennen. Dabei steht die Siedlungsentwicklung nach innen sowie die Verdichtung im Vordergrund. Der Mehrwertausgleich soll als wichtiges Instrument dienen, um der Zersiedelung entgegenzuwirken und die angestrebte Verdichtung zu unterstützen. Der Mehrwertausgleich gemäss Art. 5 RPG verlangt von den Kantonen, bedeutende Vorteile durch planungsbedingte Mehrwerte teilweise abzuschöpfen. Planungsbedingte Bodenwertsteigerungen gelten dabei als planungsbedingte Vorteile. Die Realisierung einer inneren Verdichtung ist allerdings nur möglich, wenn Grundstückseigentümer*innen und Investor*innen bereit sind, Verdichtungsprojekte umzusetzen. Insgesamt müssen bei der Umsetzung von solchen Projekten eine Vielzahl von Faktoren berücksichtigt werden, darunter die wirtschaftliche Rentabilität, die Auswirkungen auf den Immobilienmarkt sowie die Boden- und Mietpreisentwicklung. Einerseits kann die Mehrwertabgabe das Potential für eine grössere Nutzungsdichte verringern, da die Abgabe möglicherweise Anreize zur Reduzierung der Bauaktivität und damit zu einer geringeren Ausnutzung des Potenzials für eine verdichtete Entwicklung schafft, andererseits entsteht aufgrund der zahlreichen Projektrisiken eine gewisse Planungsunsicherheit. Diese Unsicherheit kann dazu führen, dass Investierende zögern, Verdichtungsprojekte zu initiieren. Die vorliegende Arbeit untersucht die Umsetzung der kommunalen Mehrwertabgabe und deren Auswirkungen auf Immobilienentwicklungen in den Gemeinden des Kantons Zürich. Dabei werden die Auswirkungen auf raumplanerische Ziele, Boden- und Mietpreise sowie die Immobilienbranche behandelt. Anhand von zwei Fallbeispielen wird mithilfe der DCF-Methode geprüft, inwiefern die Mehrwertabgabe die Wirtschaftlichkeit von verschiedenen Projektvarianten beeinflusst. Des Weiteren wird durch die Ergebnisse der Berechnungen ermittelt, ob der Mehrwertausgleich einen Anreiz für Sanierungen ohne Erweiterung und gegen Neubauten mit erhöhter Ausnützung setzt. Ausserdem wird aufgezeigt, ob durch die Mehrwertabgabe ein Anreiz gegen eine Verdichtung erfolgt. Mit der letzten Forschungsfrage wird geklärt, wie nachhaltig die finanziellen Mittel schlussendlich mittels Mehrwertausgleichsfonds eingesetzt werden. Abschliessend kann festgestellt werden, dass Ersatzneubauten mit erhöhter Ausnützung trotz der Mehrwertabgabe für Grundstückbesitzende wirtschaftlich attraktiv sind. Die Mehrwertabgabe stellt, unter der Voraussetzung einer gleichbleibenden Konjunktur kein Hindernis für eine Verdichtung dar. Wie nachhaltig die finanziellen Mittel schlussendlich eingesetzt werden, kann nicht abschliessend beurteilt werden, da noch nicht genügend Mittel verfügbar sind. Eine ganzheitliche Betrachtung der wirtschaftlichen Rentabilität, deren Auswirkungen auf den Immobilienmarkt sowie die Boden- und Mietpreisentwicklung ist erforderlich, um die Umsetzung von Verdichtungsprojekten zu unterstützen. Author: Siegl Jan Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.
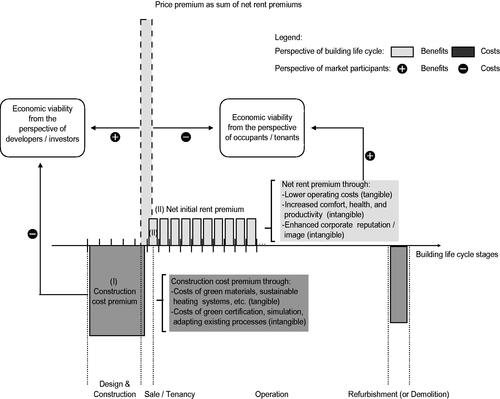
Construction Costs and Initial Yield Effects of MINERGIE Certification and Sustainable Construction Measures in New Multifamily Houses in Switzerland
Abstract In this study, the influence of MINERGIE certifications, sustainable building measures that lead to certification, and further amenities and quality measures not compulsory for certification on the construction costs and net initial (asking) rents of building projects in Switzerland is investigated. The hedonic regression results show construction cost premiums of 1.6–5.1% for MINERGIE-certified apartments. These cost premiums yield higher net initial rents of approximately 2.6–6.6*% (*not significant). In contrast, most specific sustainable building measures, such as district heating, heat pumps, or solar energy, show significant cost premiums, without higher net initial rents in the market. Whereas MINERGIE certification can translate construction costs to higher net initial rents, single sustainable construction measures do not. Such an adverse cost-benefit ratio could impede specific green investments in the short term, whereas a favorable ratio of the MINERGIE standard could promote the spread of green buildings. Link to full article: https://doi.org/10.1080/19498276.2023.2180835 Author: Kempf, Constantin. Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.
Abstract In this study, the influence of MINERGIE certifications, sustainable building measures that lead to certification, and further amenities and quality measures not compulsory for certification on the construction costs and net initial (asking) rents of building projects in Switzerland is investigated. The hedonic regression results show construction cost premiums of 1.6–5.1% for MINERGIE-certified apartments. These cost premiums yield higher net initial rents of approximately 2.6–6.6*% (*not significant). In contrast, most specific sustainable building measures, such as district heating, heat pumps, or solar energy, show significant cost premiums, without higher net initial rents in the market. Whereas MINERGIE certification can translate construction costs to higher net initial rents, single sustainable construction measures do not. Such an adverse cost-benefit ratio could impede specific green investments in the short term, whereas a favorable ratio of the MINERGIE standard could promote the spread of green buildings. Link to full article: https://doi.org/10.1080/19498276.2023.2180835 Author: Kempf, Constantin. Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.

Inventory and analysis of best practice - existing incentive programs in Switzerland and Europe
Abstract In Switzerland, political measures to achieve the nationwide climate goals set for 2050 are complex because of three layers of authorities (confederation, cantons and communes) and unharmonised responsibilities, competences and roles of cantons and municipalities. Nevertheless, the role of the commune as first point of contact for the local population is a fact. In Europe, recent programs in form of One-stop-shops have been developed and documented. The Horizon 2020 project Innovate showed very good examples and provided documents on how to set up One-stop-shops. In Switzerland, a multitude of research projects, federal and cantonal programs are currently underway, in addition to available tools. Associations such as Energiestadt or EnergieSchweiz are national platforms adapted to disseminate tools and information. In this report, examples from the canton Geneva are listed where incentive programs encouraging private property owners to renovate have been developed, such as “Onex-Rénove” and “Commune-Rénove”, supported by the Canton and the local energy provider SIG. Commune-Rénove has also been exported to the canton Vaud to three municipalities (Vevey, Morges and Nyon). The success of those initiatives relies on experts, technical but also social. Programs implementing the new roles of energy counsellor and user facilitator, assisting owners and tenants before, during and after refurbishment works, are also described here. Furthermore, some tools such as simplified building audits or cost estimations, building fact sheets with typologies and geoportals are at disposal. In some cases, guidelines for organisation of information events are published on cantonal websites. Finally, to achieve the goals of renovating a maximum of buildings as soon as possible, we need to map the current situation of stakeholders and experts. Professional associations such as the SIA (Schweizerischer Ingenieur-und Architektenverein) play a major role in the process, also banks and regional energy providers. Authors: Rinquet, Lionel; Fowler, Grit; HEPIA.
Abstract In Switzerland, political measures to achieve the nationwide climate goals set for 2050 are complex because of three layers of authorities (confederation, cantons and communes) and unharmonised responsibilities, competences and roles of cantons and municipalities. Nevertheless, the role of the commune as first point of contact for the local population is a fact. In Europe, recent programs in form of One-stop-shops have been developed and documented. The Horizon 2020 project Innovate showed very good examples and provided documents on how to set up One-stop-shops. In Switzerland, a multitude of research projects, federal and cantonal programs are currently underway, in addition to available tools. Associations such as Energiestadt or EnergieSchweiz are national platforms adapted to disseminate tools and information. In this report, examples from the canton Geneva are listed where incentive programs encouraging private property owners to renovate have been developed, such as “Onex-Rénove” and “Commune-Rénove”, supported by the Canton and the local energy provider SIG. Commune-Rénove has also been exported to the canton Vaud to three municipalities (Vevey, Morges and Nyon). The success of those initiatives relies on experts, technical but also social. Programs implementing the new roles of energy counsellor and user facilitator, assisting owners and tenants before, during and after refurbishment works, are also described here. Furthermore, some tools such as simplified building audits or cost estimations, building fact sheets with typologies and geoportals are at disposal. In some cases, guidelines for organisation of information events are published on cantonal websites. Finally, to achieve the goals of renovating a maximum of buildings as soon as possible, we need to map the current situation of stakeholders and experts. Professional associations such as the SIA (Schweizerischer Ingenieur-und Architektenverein) play a major role in the process, also banks and regional energy providers. Authors: Rinquet, Lionel; Fowler, Grit; HEPIA.
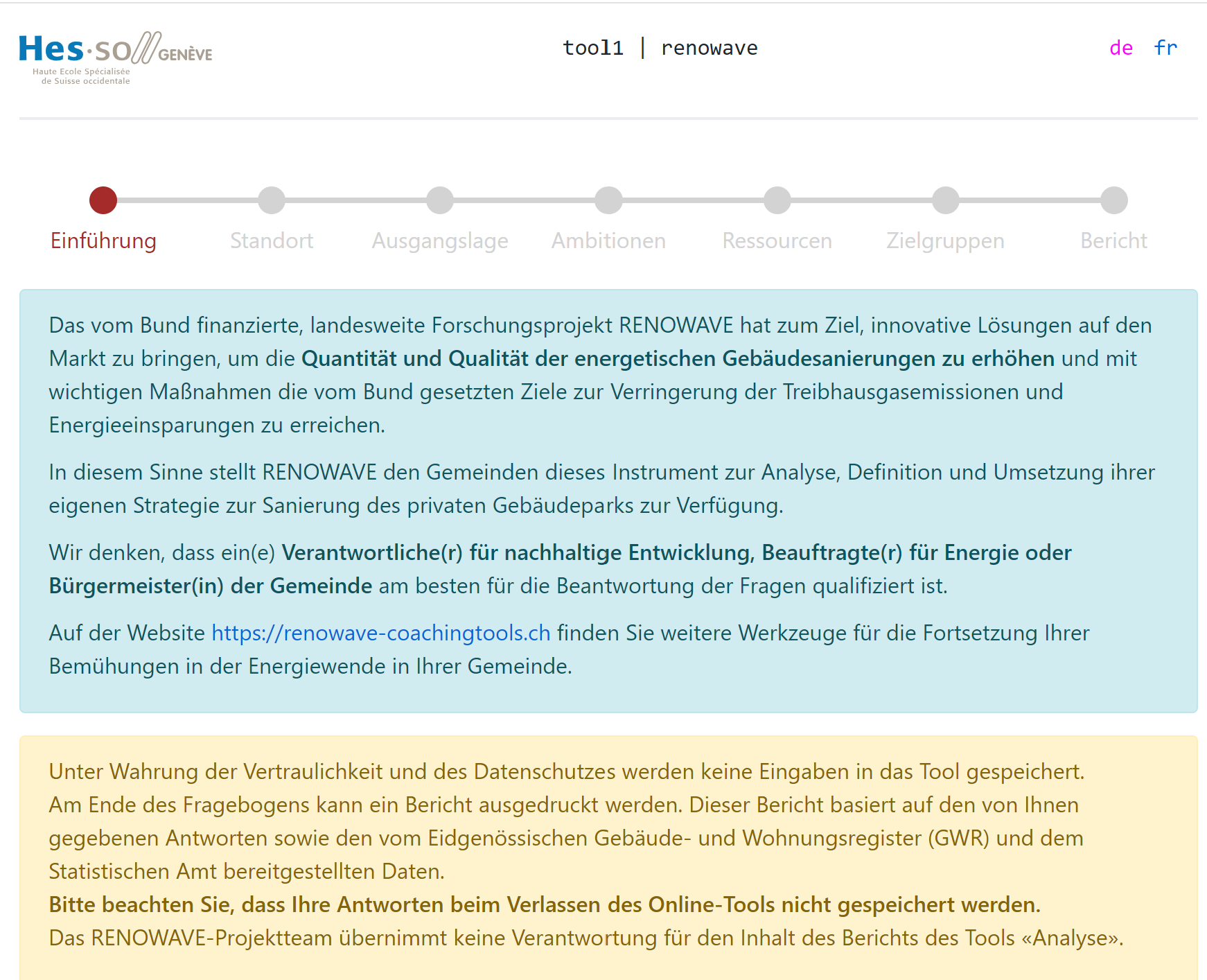
Analysis tool for municipalities
Abstract The objective of the "Analysis tool for municipalities" is to evaluate the current political and statistical situation and to determine a strategy for the municipality to support the energy renovation of private buildings. By answering a few questions on five key themes - initial situation, ambitions, resources, context and targets - this tool provides an automatic and downloadable report that includes the chosen answers as well as statistics of the built environment on a municipality’s territory. The tool is published on the website https://renowave-coachingtools.ch . This website provides a collection of open-source tools for municipalities, experts and property owners to address the issues of encouraging the renovation of private property in Switzerland. Authors: Fowler, Grit; Rinquet, Lionel; HEPIA.
Abstract The objective of the "Analysis tool for municipalities" is to evaluate the current political and statistical situation and to determine a strategy for the municipality to support the energy renovation of private buildings. By answering a few questions on five key themes - initial situation, ambitions, resources, context and targets - this tool provides an automatic and downloadable report that includes the chosen answers as well as statistics of the built environment on a municipality’s territory. The tool is published on the website https://renowave-coachingtools.ch . This website provides a collection of open-source tools for municipalities, experts and property owners to address the issues of encouraging the renovation of private property in Switzerland. Authors: Fowler, Grit; Rinquet, Lionel; HEPIA.

Die energetische Sanierung von Gebäuden
Abstract In der Schweiz wird derzeit rund ein Fünftel der CO2-Emissionen durch den Betrieb von Gebäuden verursacht. Entsprechend relevant sind Bestrebungen, diese Emissionen zu reduzieren. Eine von mehreren Reduzierungsstrategien greift bei der Betriebsenergie an: Durch «energetische Sanierungen» soll der Verbrauch bei bestehenden Gebäuden reduziert werden. Welche Massnahmen fallen darunter? Wie ist der rechtliche Rahmen für solche Sanierungen ausgestaltet? Wie stehen Bundesrecht, kantonale Regelungen und private technische Normen zueinander? Kann der Staat unterstützende Funktionen übernehmen? Zu diesen Fragen liefert der vorliegende Band einen Überblick. Er erleichtert Juristinnen und Juristen genauso wie Personen aus unterschiedlichen Praxisfeldern eine Annäherung an das Thema aus juristischer Sicht. Die Veröffentlichungen zum Energierecht Band 32 finden Sie hier: https://www.dike.ch/streiff-trajkova-huser-energetische-sanierung?srsltid=AfmBOorJZYmth7GbNfRm6CRP8ln1n4R6iwkX26rNTouyvF1XFoNmGhA4&___store=en&___from_store=de. Authors: Streiff, Oliver; Trajkova, Renata; Huser, Meinrad.
Abstract In der Schweiz wird derzeit rund ein Fünftel der CO2-Emissionen durch den Betrieb von Gebäuden verursacht. Entsprechend relevant sind Bestrebungen, diese Emissionen zu reduzieren. Eine von mehreren Reduzierungsstrategien greift bei der Betriebsenergie an: Durch «energetische Sanierungen» soll der Verbrauch bei bestehenden Gebäuden reduziert werden. Welche Massnahmen fallen darunter? Wie ist der rechtliche Rahmen für solche Sanierungen ausgestaltet? Wie stehen Bundesrecht, kantonale Regelungen und private technische Normen zueinander? Kann der Staat unterstützende Funktionen übernehmen? Zu diesen Fragen liefert der vorliegende Band einen Überblick. Er erleichtert Juristinnen und Juristen genauso wie Personen aus unterschiedlichen Praxisfeldern eine Annäherung an das Thema aus juristischer Sicht. Die Veröffentlichungen zum Energierecht Band 32 finden Sie hier: https://www.dike.ch/streiff-trajkova-huser-energetische-sanierung?srsltid=AfmBOorJZYmth7GbNfRm6CRP8ln1n4R6iwkX26rNTouyvF1XFoNmGhA4&___store=en&___from_store=de. Authors: Streiff, Oliver; Trajkova, Renata; Huser, Meinrad.
Grenzen privater Regulierung am Beispiel der energetischen Gebäudesanierung
In ihrem Vortrag an der Energie- und Nachhaltigkeitstagung 2024 der ZHAW thematisierte Dr. iur. Renata Trajkova die Grenzen privater Regulierung am Beispiel der energetischen Gebäudesanierung. In diesem Bereich werden Bundesrecht, kantonale Erlasse und private technische Normen gleichzeitig angewendet. Auf die Vollzugsprobleme hat der Bund hat mit Art. 45 EnG reagiert. Dabei hat er gestützt auf Art. 89 BV in teils wohl kompetenzwidriger Weise in die Zuständigkeit der Kantone eingegriffen. Die dringend notwendigen energetischen Gebäudesanierungen wurden auf diese Weise vom Bund zwar gefördert. Zugleich werfen die Massnahmen aber verfassungsmässig heikle Fragen auf.
In ihrem Vortrag an der Energie- und Nachhaltigkeitstagung 2024 der ZHAW thematisierte Dr. iur. Renata Trajkova die Grenzen privater Regulierung am Beispiel der energetischen Gebäudesanierung. In diesem Bereich werden Bundesrecht, kantonale Erlasse und private technische Normen gleichzeitig angewendet. Auf die Vollzugsprobleme hat der Bund hat mit Art. 45 EnG reagiert. Dabei hat er gestützt auf Art. 89 BV in teils wohl kompetenzwidriger Weise in die Zuständigkeit der Kantone eingegriffen. Die dringend notwendigen energetischen Gebäudesanierungen wurden auf diese Weise vom Bund zwar gefördert. Zugleich werfen die Massnahmen aber verfassungsmässig heikle Fragen auf.
2. Tagung zum Energie- und Nachhaltigkeitsrecht – Grenzen der Regulierung
Abstract Im Energierecht dienen staatliche Regulierungen traditionell der technischen Sicherheit sowie der Versorgungssicherheit. Mit dem Energieartikel in der Bundesverfassung, dem ersten Liberalisierungsschritt im Strommarkt in den 2000er Jahren und spätestens seit der Energiestrategie 2050 sind die energiepolitischen Zielsetzungen massgeblich erweitert worden: Der Staat setzt auch umweltpolitische Vorgaben, fördert neue Technologien und beeinflusst Märkte. Mit der politisch angestrebten Transformation soll ein fundamentaler technischer, ökonomischer und sozialer Wandel erreicht werden. In ihrem Vortrag an der Energie- und Nachhaltigkeitstagung 2024 der ZHAW thematisierte Dr. iur. Renata Trajkova die Grenzen privater Regulierung am Beispiel der energetischen Gebäudesanierung. In diesem Bereich werden Bundesrecht, kantonale Erlasse und private technische Normen gleichzeitig angewendet. Auf die Vollzugsprobleme hat der Bund hat mit Art. 45 EnG reagiert. Dabei hat er gestützt auf Art. 89 BV in teils wohl kompetenzwidriger Weise in die Zuständigkeit der Kantone eingegriffen. Die dringend notwendigen energetischen Gebäudesanierungen wurden auf diese Weise vom Bund zwar gefördert. Zugleich werfen die Massnahmen aber verfassungsmässig heikle Fragen auf. Authors: Paggiola, Elia; Pantano, Lara. Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.
Abstract Im Energierecht dienen staatliche Regulierungen traditionell der technischen Sicherheit sowie der Versorgungssicherheit. Mit dem Energieartikel in der Bundesverfassung, dem ersten Liberalisierungsschritt im Strommarkt in den 2000er Jahren und spätestens seit der Energiestrategie 2050 sind die energiepolitischen Zielsetzungen massgeblich erweitert worden: Der Staat setzt auch umweltpolitische Vorgaben, fördert neue Technologien und beeinflusst Märkte. Mit der politisch angestrebten Transformation soll ein fundamentaler technischer, ökonomischer und sozialer Wandel erreicht werden. In ihrem Vortrag an der Energie- und Nachhaltigkeitstagung 2024 der ZHAW thematisierte Dr. iur. Renata Trajkova die Grenzen privater Regulierung am Beispiel der energetischen Gebäudesanierung. In diesem Bereich werden Bundesrecht, kantonale Erlasse und private technische Normen gleichzeitig angewendet. Auf die Vollzugsprobleme hat der Bund hat mit Art. 45 EnG reagiert. Dabei hat er gestützt auf Art. 89 BV in teils wohl kompetenzwidriger Weise in die Zuständigkeit der Kantone eingegriffen. Die dringend notwendigen energetischen Gebäudesanierungen wurden auf diese Weise vom Bund zwar gefördert. Zugleich werfen die Massnahmen aber verfassungsmässig heikle Fragen auf. Authors: Paggiola, Elia; Pantano, Lara. Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.
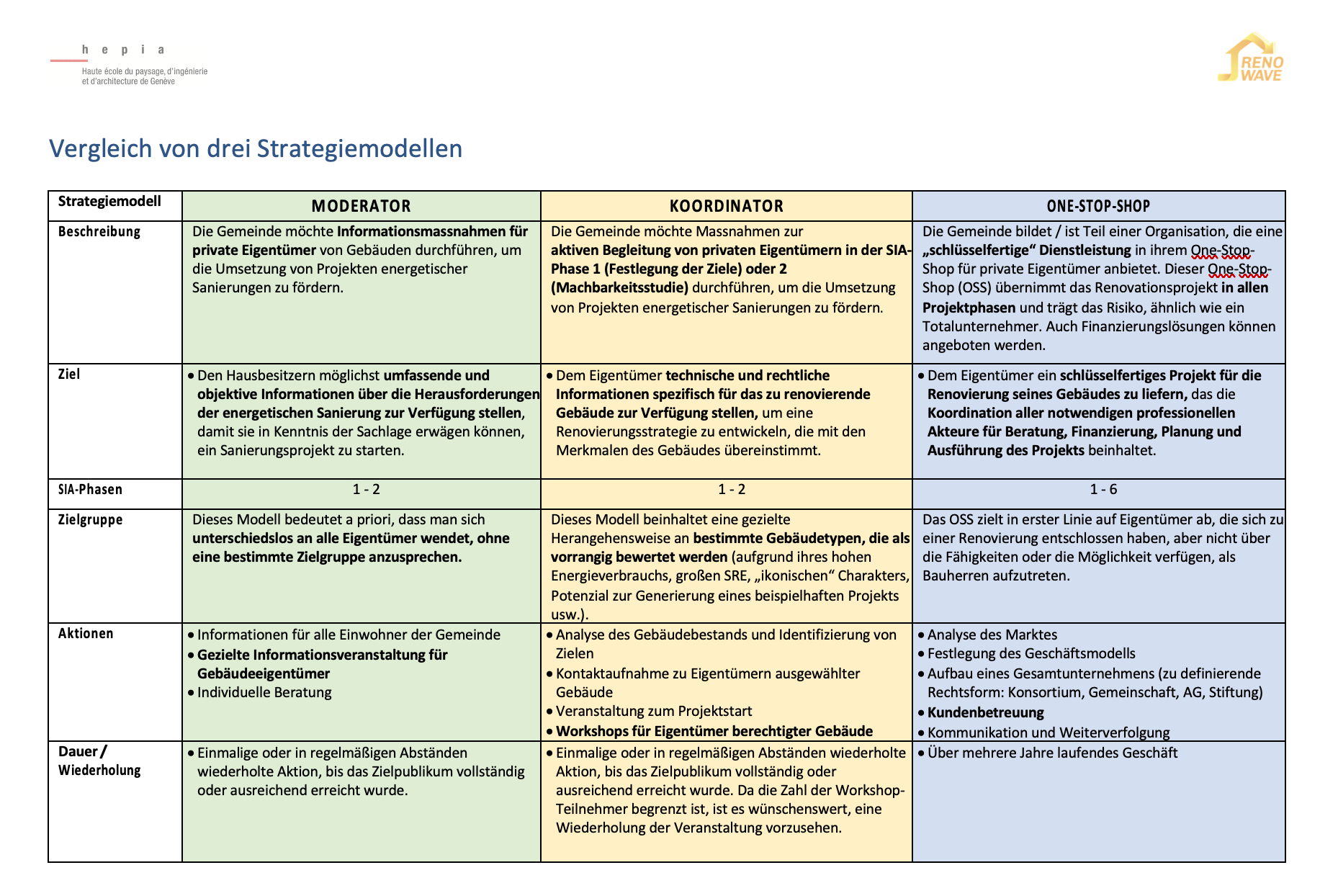
Strategy models for municipalities to promote renovation of private properties
Abstract In this overview, we describe three strategy models which are currently used in Switzerland and Europe and which Swiss municipalities could use to promote the renovation of private properties : "moderator", "coordinator" or "one-stop-shop". The following table summarises the objectives, advantages and disadvantages of these three strategy models. Tools 2A ‘MODERATOR’ and 2B ‘COORDINATOR’ (see other opportunities) describe in detail the processes required to implement these models. The One-Stop-Shop model (OSS) was analyzed and is described in the table. However, it will not be further developed as part of the RENOWAVE project. In discussions with local partners, this model was assessed as impractical, as it does not correspond to the political culture of Swiss municipalities. Authors: Fowler, Grit; Rinquet, Lionel; HEPIA.
Abstract In this overview, we describe three strategy models which are currently used in Switzerland and Europe and which Swiss municipalities could use to promote the renovation of private properties : "moderator", "coordinator" or "one-stop-shop". The following table summarises the objectives, advantages and disadvantages of these three strategy models. Tools 2A ‘MODERATOR’ and 2B ‘COORDINATOR’ (see other opportunities) describe in detail the processes required to implement these models. The One-Stop-Shop model (OSS) was analyzed and is described in the table. However, it will not be further developed as part of the RENOWAVE project. In discussions with local partners, this model was assessed as impractical, as it does not correspond to the political culture of Swiss municipalities. Authors: Fowler, Grit; Rinquet, Lionel; HEPIA.
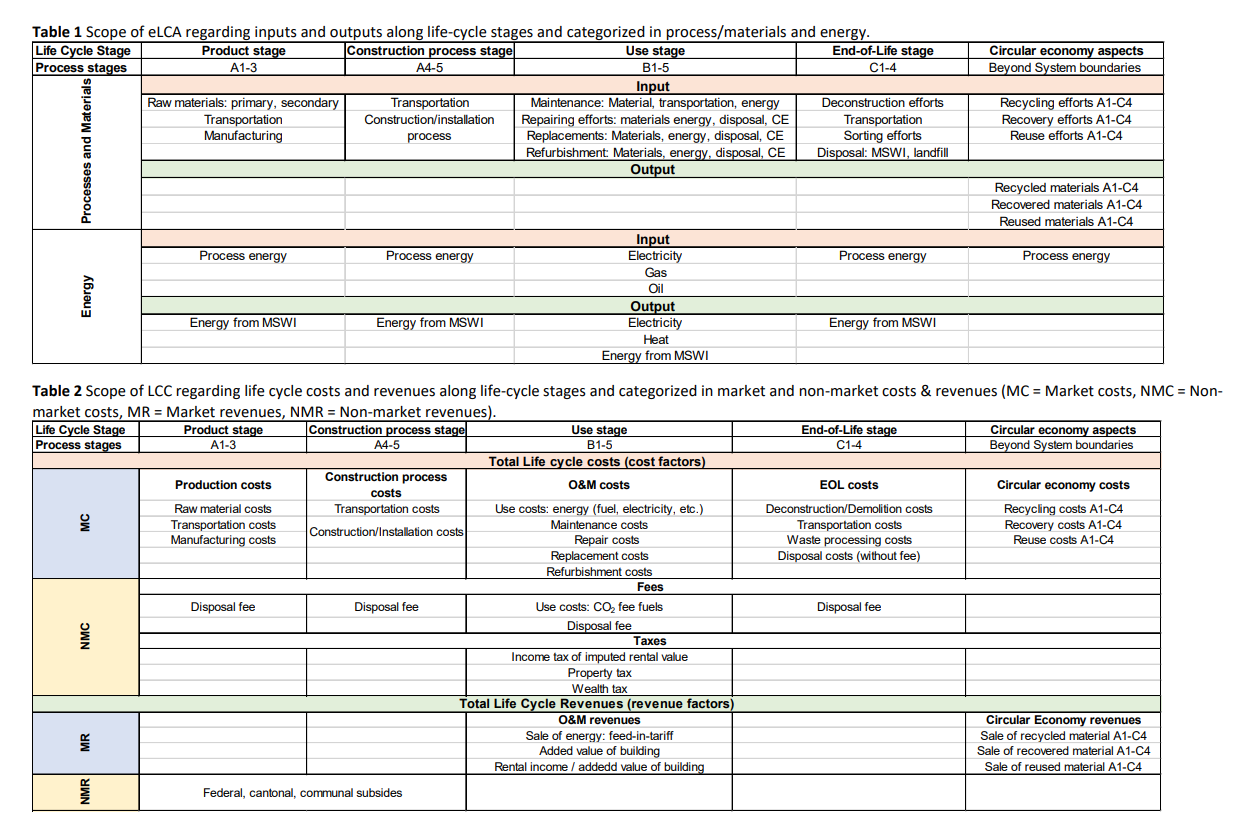
Report on Initial Lifecycle Sustainability Assessment- Framework and comprehensive list of Sustainability Indicators
Abstract In Switzerland, buildings are one of the major sources of CO2 emissions accounting for ~24% of the total. Therefore, to achieve the requests posed by the Paris agreement, these emissions need to be reduced. In this context, this can be achieved either by efficient envelopes (reduction of energy demand) and/or by switching from fossil fuels to renewable energies. While such measures are straightforward in the case of new buildings, retrofit of the existing building stock is more complex. The RENOWAVE project aims at boosting the retrofit of the Swiss building stock, both in terms of quantity (renovation rate) and quality (performance), as to help achieve the objectives formulated for the building sector in the Swiss long-term climate strategy. To accomplish this goal a holistic, value-chain oriented approach is adopted in RENOWAVE to contribute achieving several SDGs including socio-economic as well as environmental ones (7,8,12,13). The holistic approach aims at solving several multifaceted, interrelated, and transdisciplinary challenges that rise from the massive and efficient retrofit of the existing Swiss building stock. These challenges have been allocated to several individual sub-projects (SPs) clustered in different thematic pillars in RENOWAVE. In SP1.4 a comprehensive sustainability framework specifically tailored to the sustainability, resilience and decarbonization targets and policies of the Swiss government and consider the needs and perspectives of the diverse stakeholders in the building sector is derived. The final aim of SP1.4 is to realize a tool that allows stakeholders to compare different potential renovation measures with respect to the current state of the building under interest by means of providing ranking and scores of each alternative. This report presents the initial development of such a tool, called Life-Cycle Sustainability Assessment-Framework (LCSA-F), for multifamily houses renovation measures. The LCSA-F combined the Environmental Life Cycle Assessment (eLCA), Life Cycle Cost (LCC), Social Life Cycle Assessment (sLCA) and Resilience Assessment (RA) domains within the overarching Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) method. Therefore, the tool makes use of one of the main family of MCDA methods, which is represented by composite indicators (CIs), or indices, since it leads to a score of the alternatives that can then be easily ranked. The initial development of the proposed framework was achieved in close collaboration with a group of 8 experts from academia, construction enterprises, consulting, etc., to grasp the heterogeneous knowledges and interests from these different domains. Particularly, the experts participated to 2 workshops to help defining the proposed framework. In the 1st workshop the experts were asked to define the system boundaries of the framework and their level of details. In this context, the group uniformly voted for covering the whole life cycle including the product stage, the construction process stage, the use stage, and the end-of-life stage as well as presenting all results at the process stage level. Furthermore, the experts voted the functional unit (FU) for the LCSA-F, which results to be “heated area per year of building lifetime” due to its wide application in the Swiss building context expressing the building’s energy demand. Moreover, during the 1st Workshop, the group of experts selected the criteria to be included in the framework, since CIs are based on an aggregation of criteria that measure different domains. In this context, the framework presented here is based on a hierarchical structure of the criteria, which is composed by 3 layers. In the first layer the four abovementioned domains, i.e., eLCA, LCC, sLCA, RA, are present. The second layer is composed by a set of 16 criteria, subdivided into 5 for eLCA and sLCA, 4 for RA and 2 for LCC, which were defined based on a comprehensive literature review and the expert selection during the 1st Workshop. The 3rd layer of the hierarchical structure of the framework contains a set of 56 subcriteria, subdivided into 10 for eLCA and sLCA, 9 for LCC and 27 for RA, which were selected based on a comprehensive literature review and in accordance with the group of experts. Once the criteria hierarchical structure of the LCSA-F was defined, during the 2nd Workshop, the experts were asked to weight the 2nd and 3rd level of the hierarchy to build a default preference profile, different to the equal weight one, to be included in the tool under development. Finally, based on the problem type, the criteria and sub-criteria nature, the preference elicitation, and the features of aggregation under interest, the most reasonable MCDA method for the tool under development was selected. In this context, the MultiAttribute Value Theory (MAVT) was found to be the best methodological solution based on the MCDA-MSS tool. Authors: Baumgartner, Corinna; Lobsiger-Kägi, Evelyn; Spada, Matteo.
Abstract In Switzerland, buildings are one of the major sources of CO2 emissions accounting for ~24% of the total. Therefore, to achieve the requests posed by the Paris agreement, these emissions need to be reduced. In this context, this can be achieved either by efficient envelopes (reduction of energy demand) and/or by switching from fossil fuels to renewable energies. While such measures are straightforward in the case of new buildings, retrofit of the existing building stock is more complex. The RENOWAVE project aims at boosting the retrofit of the Swiss building stock, both in terms of quantity (renovation rate) and quality (performance), as to help achieve the objectives formulated for the building sector in the Swiss long-term climate strategy. To accomplish this goal a holistic, value-chain oriented approach is adopted in RENOWAVE to contribute achieving several SDGs including socio-economic as well as environmental ones (7,8,12,13). The holistic approach aims at solving several multifaceted, interrelated, and transdisciplinary challenges that rise from the massive and efficient retrofit of the existing Swiss building stock. These challenges have been allocated to several individual sub-projects (SPs) clustered in different thematic pillars in RENOWAVE. In SP1.4 a comprehensive sustainability framework specifically tailored to the sustainability, resilience and decarbonization targets and policies of the Swiss government and consider the needs and perspectives of the diverse stakeholders in the building sector is derived. The final aim of SP1.4 is to realize a tool that allows stakeholders to compare different potential renovation measures with respect to the current state of the building under interest by means of providing ranking and scores of each alternative. This report presents the initial development of such a tool, called Life-Cycle Sustainability Assessment-Framework (LCSA-F), for multifamily houses renovation measures. The LCSA-F combined the Environmental Life Cycle Assessment (eLCA), Life Cycle Cost (LCC), Social Life Cycle Assessment (sLCA) and Resilience Assessment (RA) domains within the overarching Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) method. Therefore, the tool makes use of one of the main family of MCDA methods, which is represented by composite indicators (CIs), or indices, since it leads to a score of the alternatives that can then be easily ranked. The initial development of the proposed framework was achieved in close collaboration with a group of 8 experts from academia, construction enterprises, consulting, etc., to grasp the heterogeneous knowledges and interests from these different domains. Particularly, the experts participated to 2 workshops to help defining the proposed framework. In the 1st workshop the experts were asked to define the system boundaries of the framework and their level of details. In this context, the group uniformly voted for covering the whole life cycle including the product stage, the construction process stage, the use stage, and the end-of-life stage as well as presenting all results at the process stage level. Furthermore, the experts voted the functional unit (FU) for the LCSA-F, which results to be “heated area per year of building lifetime” due to its wide application in the Swiss building context expressing the building’s energy demand. Moreover, during the 1st Workshop, the group of experts selected the criteria to be included in the framework, since CIs are based on an aggregation of criteria that measure different domains. In this context, the framework presented here is based on a hierarchical structure of the criteria, which is composed by 3 layers. In the first layer the four abovementioned domains, i.e., eLCA, LCC, sLCA, RA, are present. The second layer is composed by a set of 16 criteria, subdivided into 5 for eLCA and sLCA, 4 for RA and 2 for LCC, which were defined based on a comprehensive literature review and the expert selection during the 1st Workshop. The 3rd layer of the hierarchical structure of the framework contains a set of 56 subcriteria, subdivided into 10 for eLCA and sLCA, 9 for LCC and 27 for RA, which were selected based on a comprehensive literature review and in accordance with the group of experts. Once the criteria hierarchical structure of the LCSA-F was defined, during the 2nd Workshop, the experts were asked to weight the 2nd and 3rd level of the hierarchy to build a default preference profile, different to the equal weight one, to be included in the tool under development. Finally, based on the problem type, the criteria and sub-criteria nature, the preference elicitation, and the features of aggregation under interest, the most reasonable MCDA method for the tool under development was selected. In this context, the MultiAttribute Value Theory (MAVT) was found to be the best methodological solution based on the MCDA-MSS tool. Authors: Baumgartner, Corinna; Lobsiger-Kägi, Evelyn; Spada, Matteo.
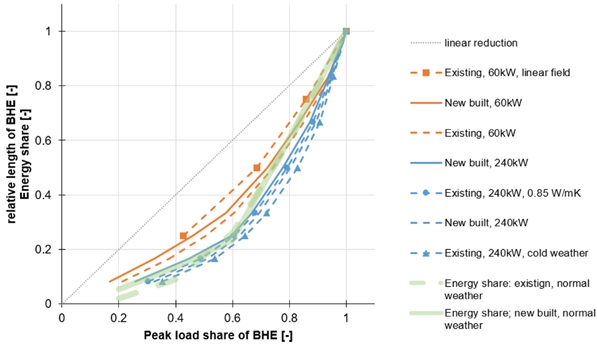
HP Source - Integration options for heat sources
Abstract With a massive expansion of heat pumps, good heat sources are also required for high efficiency. Particularly in the higher output range above 50 kW and in densely built-up areas, individual heat sources such as outside air or the ground have limitations in terms of noise, space and drilling depth. In the HP-source project, integration options for heat sources were investigated using system simulations with the aim of overcoming the restrictions of individual heat sources and enabling monovalent heat pump operation with high efficiency. The focus was set on two strategies: A peak load coverage, in which both sources are designed to cover part of the heating capacity and the ground source is switched on for the peak load in winter, and a regeneration, in which the ground source is regenerated in summer and in the transition period by a second source, which can also be operated as sole heat source in summer. It was found that both strategies can overcome the limitations of individual sources and that performance and cost benefits can be exploited through synergies and design advantages between the sources, which can even overcompensate for the additional costs of integrating a second heat source, making multi-source systems also interesting for the use without restrictions. Both with peak load coverage and with regeneration, probe fields can also be designed significantly smaller overcoming space and drilling depth limitations. Full report in German: https://www.aramis.admin.ch/Default?DocumentID=71345&Load=true Authors: Wemhöner, Carsten; Meier, Christoph; Büsser, Simon; Bätschmann, Marc. Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.
Abstract With a massive expansion of heat pumps, good heat sources are also required for high efficiency. Particularly in the higher output range above 50 kW and in densely built-up areas, individual heat sources such as outside air or the ground have limitations in terms of noise, space and drilling depth. In the HP-source project, integration options for heat sources were investigated using system simulations with the aim of overcoming the restrictions of individual heat sources and enabling monovalent heat pump operation with high efficiency. The focus was set on two strategies: A peak load coverage, in which both sources are designed to cover part of the heating capacity and the ground source is switched on for the peak load in winter, and a regeneration, in which the ground source is regenerated in summer and in the transition period by a second source, which can also be operated as sole heat source in summer. It was found that both strategies can overcome the limitations of individual sources and that performance and cost benefits can be exploited through synergies and design advantages between the sources, which can even overcompensate for the additional costs of integrating a second heat source, making multi-source systems also interesting for the use without restrictions. Both with peak load coverage and with regeneration, probe fields can also be designed significantly smaller overcoming space and drilling depth limitations. Full report in German: https://www.aramis.admin.ch/Default?DocumentID=71345&Load=true Authors: Wemhöner, Carsten; Meier, Christoph; Büsser, Simon; Bätschmann, Marc. Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.

P&D Renosource – Multi-source heat pump system for the boiler replacement with ground probes for peak load coverage
Abstract The project investigates a boiler replacement in two multi-family dwellings, where the oil boilers are replaced by indoor installed propane heat pumps with the two heat sources air and a peak load coverage by borehole heat exchangers. By designing the ground source for peak coverage, existing space and drilling depth constraints are overcome and the heat pump is operated without fossil fuel peak coverage. This is also supported by the high possible flow temperatures of 70 °C of the propane heat pumps. The monitoring of the heat pumps over three heating periods therefore serves not only for operational evaluation and optimization, but also for the verification of simulation models, which are used to develop advanced design and planning recommendations for these multi-source systems. Furthermore, an evaluation of indoor propane heat pumps with regard to efficiency and economy will be performed. The goal is to document a best practice system for multi-source applications and indoor installed propane heat pumps. Authors: Wemhöner, Carsten; Meier, Christoph. Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.
Abstract The project investigates a boiler replacement in two multi-family dwellings, where the oil boilers are replaced by indoor installed propane heat pumps with the two heat sources air and a peak load coverage by borehole heat exchangers. By designing the ground source for peak coverage, existing space and drilling depth constraints are overcome and the heat pump is operated without fossil fuel peak coverage. This is also supported by the high possible flow temperatures of 70 °C of the propane heat pumps. The monitoring of the heat pumps over three heating periods therefore serves not only for operational evaluation and optimization, but also for the verification of simulation models, which are used to develop advanced design and planning recommendations for these multi-source systems. Furthermore, an evaluation of indoor propane heat pumps with regard to efficiency and economy will be performed. The goal is to document a best practice system for multi-source applications and indoor installed propane heat pumps. Authors: Wemhöner, Carsten; Meier, Christoph. Note: This result was developed outside of the Renowave project.
Evaluation of qualitative influencing factors
Abstract The SIA 480 standard focuses on the widely used classic investment calculation methods for the profitability calculation. However, these are only one of the criteria that should be considered when assessing a project. Investments also have non-monetary effects and projects often differ in terms of factors that are hardly taken into account in the monetary assessment. Our aim is to identify and evaluate these soft criteria. The enclosed article shows our thoughts on the relevant terminology and a possible evaluation method. Authors: Brigger, Sabine; King, Marvin; HSLU.
Abstract The SIA 480 standard focuses on the widely used classic investment calculation methods for the profitability calculation. However, these are only one of the criteria that should be considered when assessing a project. Investments also have non-monetary effects and projects often differ in terms of factors that are hardly taken into account in the monetary assessment. Our aim is to identify and evaluate these soft criteria. The enclosed article shows our thoughts on the relevant terminology and a possible evaluation method. Authors: Brigger, Sabine; King, Marvin; HSLU.
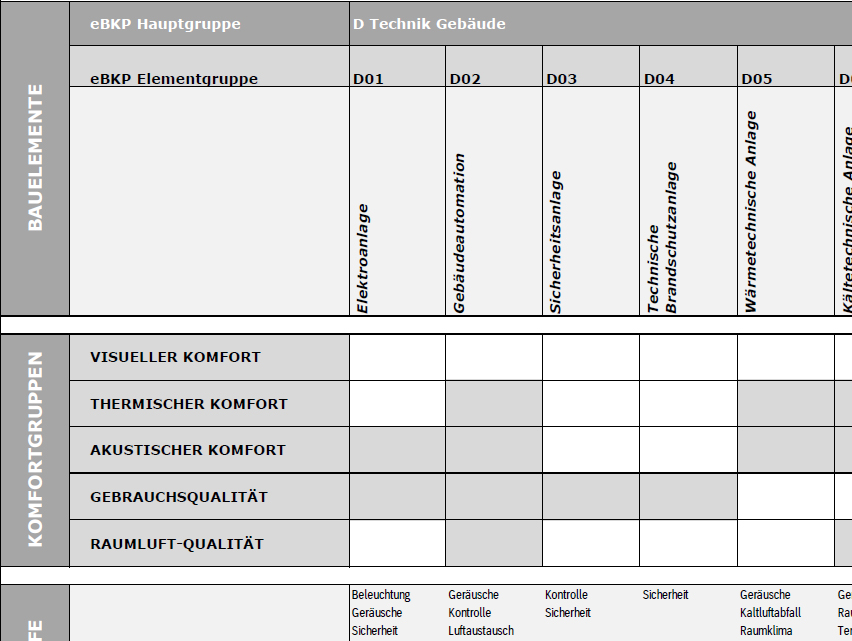
Soft factors as added value in refurbishments
Abstract When refurbishing a building, “hard factors” are usually considered, which usually bring material or quantifiable added value. The “soft factors”, which bring added value in terms of quality and comfort but are not directly quantifiable, are not taken into account. This neglect can mean that the comprehensive added value of refurbishments for (private) owners and tenants is not fully captured and therefore the benefits of refurbishments are underestimated. In the exemplary excerpt from the attached list, comfort groups - visual, thermal, acoustic comfort as well as quality of use and indoor air quality - are linked to element groups and associated quality terms are added. This is intended to make the soft factors in refurbishments visible. The attached excerpt includes the element groups (basis eBKP-H) “D Building technology” and “E External wall cladding of buildings”. Authors: Brigger, Sabine; King, Marvin; HSLU.
Abstract When refurbishing a building, “hard factors” are usually considered, which usually bring material or quantifiable added value. The “soft factors”, which bring added value in terms of quality and comfort but are not directly quantifiable, are not taken into account. This neglect can mean that the comprehensive added value of refurbishments for (private) owners and tenants is not fully captured and therefore the benefits of refurbishments are underestimated. In the exemplary excerpt from the attached list, comfort groups - visual, thermal, acoustic comfort as well as quality of use and indoor air quality - are linked to element groups and associated quality terms are added. This is intended to make the soft factors in refurbishments visible. The attached excerpt includes the element groups (basis eBKP-H) “D Building technology” and “E External wall cladding of buildings”. Authors: Brigger, Sabine; King, Marvin; HSLU.

La part sociale de la renovation énergétique. Une enquête auprès des habitants.
Abstract Le présent article s’intéresse au processus de rénovation énergétique du bâti existant. Afin de comprendre en quoi consiste ce processus et de quelles manières il entretient d’étroites relations avec la pratique professionnelle des travailleurs sociaux, nous avons souhaité mettre en valeur le point de vue des habitants. Quel est le rapport des habitants à la rénovation énergétique ? Quelles sont les formes d’accompagnement social mises en place et quel rôle pour les travailleurs sociaux ? Et qu’en est-il des inégalités sociales et de leur potentielle résorption ? Parce que la rénovation énergétique a pour particularité de poser des questions à la fois énergétiques. et extra-énergétiques, elle affecte à la fois le lieu de vie habité ainsi que la personne qui l’habite. De là, au regard de l’utilité publique de l’accompagnement social de la rénovation énergétique du bâti, il nous semble qu’il devrait être inclus dans l’organisation institutionnelle du travail social et de ses missions. Authors: Gaberell, Simon (HETS-GE); Harchi, Kaoutar(HETS-GE).
Abstract Le présent article s’intéresse au processus de rénovation énergétique du bâti existant. Afin de comprendre en quoi consiste ce processus et de quelles manières il entretient d’étroites relations avec la pratique professionnelle des travailleurs sociaux, nous avons souhaité mettre en valeur le point de vue des habitants. Quel est le rapport des habitants à la rénovation énergétique ? Quelles sont les formes d’accompagnement social mises en place et quel rôle pour les travailleurs sociaux ? Et qu’en est-il des inégalités sociales et de leur potentielle résorption ? Parce que la rénovation énergétique a pour particularité de poser des questions à la fois énergétiques. et extra-énergétiques, elle affecte à la fois le lieu de vie habité ainsi que la personne qui l’habite. De là, au regard de l’utilité publique de l’accompagnement social de la rénovation énergétique du bâti, il nous semble qu’il devrait être inclus dans l’organisation institutionnelle du travail social et de ses missions. Authors: Gaberell, Simon (HETS-GE); Harchi, Kaoutar(HETS-GE).
Livret illustré : Accompagner les habitant·es lors d'une rénovation énergétique
Abstract Le présent livret explicite, étape après étape, l'expérience de la rénovation énergétique du bâti existant selon le point de vue d’un·e habitant·e. En recourant à l’illustration, en mettant en scène des personnages, en usant d’un langage simple, nous avons souhaité imaginer ce à quoi pourrait ressembler un accompagnement social pris en charge par des professionnel·les à l’écoute des habitant·es. Plus encore, nous avons cherché à rendre visible l’ensemble de ses apports bénéfiques. Authors: Gaberell, Simon (HETS-GE); Harchi, Kaoutar (HETS-GE).
Abstract Le présent livret explicite, étape après étape, l'expérience de la rénovation énergétique du bâti existant selon le point de vue d’un·e habitant·e. En recourant à l’illustration, en mettant en scène des personnages, en usant d’un langage simple, nous avons souhaité imaginer ce à quoi pourrait ressembler un accompagnement social pris en charge par des professionnel·les à l’écoute des habitant·es. Plus encore, nous avons cherché à rendre visible l’ensemble de ses apports bénéfiques. Authors: Gaberell, Simon (HETS-GE); Harchi, Kaoutar (HETS-GE).

Poster illustré: Accompagner les habitant·es lors d'une rénovation énergétique
Abstract Le présent poster présente, de façon synthétique et illustrée, le processus de la rénovation énergétique selon le point de vue d'un.habitant.e. Authors: Gaberell, Simon (HETS-GE); Harchi, Kaoutar (HETS-GE).
Abstract Le présent poster présente, de façon synthétique et illustrée, le processus de la rénovation énergétique selon le point de vue d'un.habitant.e. Authors: Gaberell, Simon (HETS-GE); Harchi, Kaoutar (HETS-GE).

One-Stop-Shop for energy-efficient refurbishment
Abstract As result of numerous discussions and work within the NettoNull-Kollektiv and the Renowave project, we’re now launching an offer as a one-stop-shop for energy-efficient refurbishments: fossil fuel heating replacement, basement and roof insulation, photovoltaics and infrastructure for electromobility - all from a single point of contact. Including an efficient operation trough operation module and specific add-ons. For more information: https://www.tend.ch/de/services/umsetzen-betreiben/energetische-sanierung. Author: Bätschmann, Marc.
Abstract As result of numerous discussions and work within the NettoNull-Kollektiv and the Renowave project, we’re now launching an offer as a one-stop-shop for energy-efficient refurbishments: fossil fuel heating replacement, basement and roof insulation, photovoltaics and infrastructure for electromobility - all from a single point of contact. Including an efficient operation trough operation module and specific add-ons. For more information: https://www.tend.ch/de/services/umsetzen-betreiben/energetische-sanierung. Author: Bätschmann, Marc.
Prendre en charge la part sociale de la rénovation énergétique : une nécessité.
Abstract La nécessité de rénover le parc bâti existant afin de réduire la consommation d’énergies fossiles est désormais reconnue et soutenue par des politiques publiques ainsi que par un cadre légal spécifique. Or pareille transition ne va pas sans affecter, et de diverses manières, le quotidien des habitant-es. Le présent document vise à mettre évidence une nécessité complémentaire : prendre en charge la part sociale de la rénovation énergétique. Pour cela, nous nous appuierons sur trois enquêtes de terrain réalisées entre 2021 et 2024 , et centrerons notre propos sur l’activité d’accompagnement social – soit la mise en place d’un ensemble d’actions de soutien aux habitant-es. Authors : Gaberell, Simon (HETS-GE); Harchi, Kaoutar(HETS-GE).
Abstract La nécessité de rénover le parc bâti existant afin de réduire la consommation d’énergies fossiles est désormais reconnue et soutenue par des politiques publiques ainsi que par un cadre légal spécifique. Or pareille transition ne va pas sans affecter, et de diverses manières, le quotidien des habitant-es. Le présent document vise à mettre évidence une nécessité complémentaire : prendre en charge la part sociale de la rénovation énergétique. Pour cela, nous nous appuierons sur trois enquêtes de terrain réalisées entre 2021 et 2024 , et centrerons notre propos sur l’activité d’accompagnement social – soit la mise en place d’un ensemble d’actions de soutien aux habitant-es. Authors : Gaberell, Simon (HETS-GE); Harchi, Kaoutar(HETS-GE).
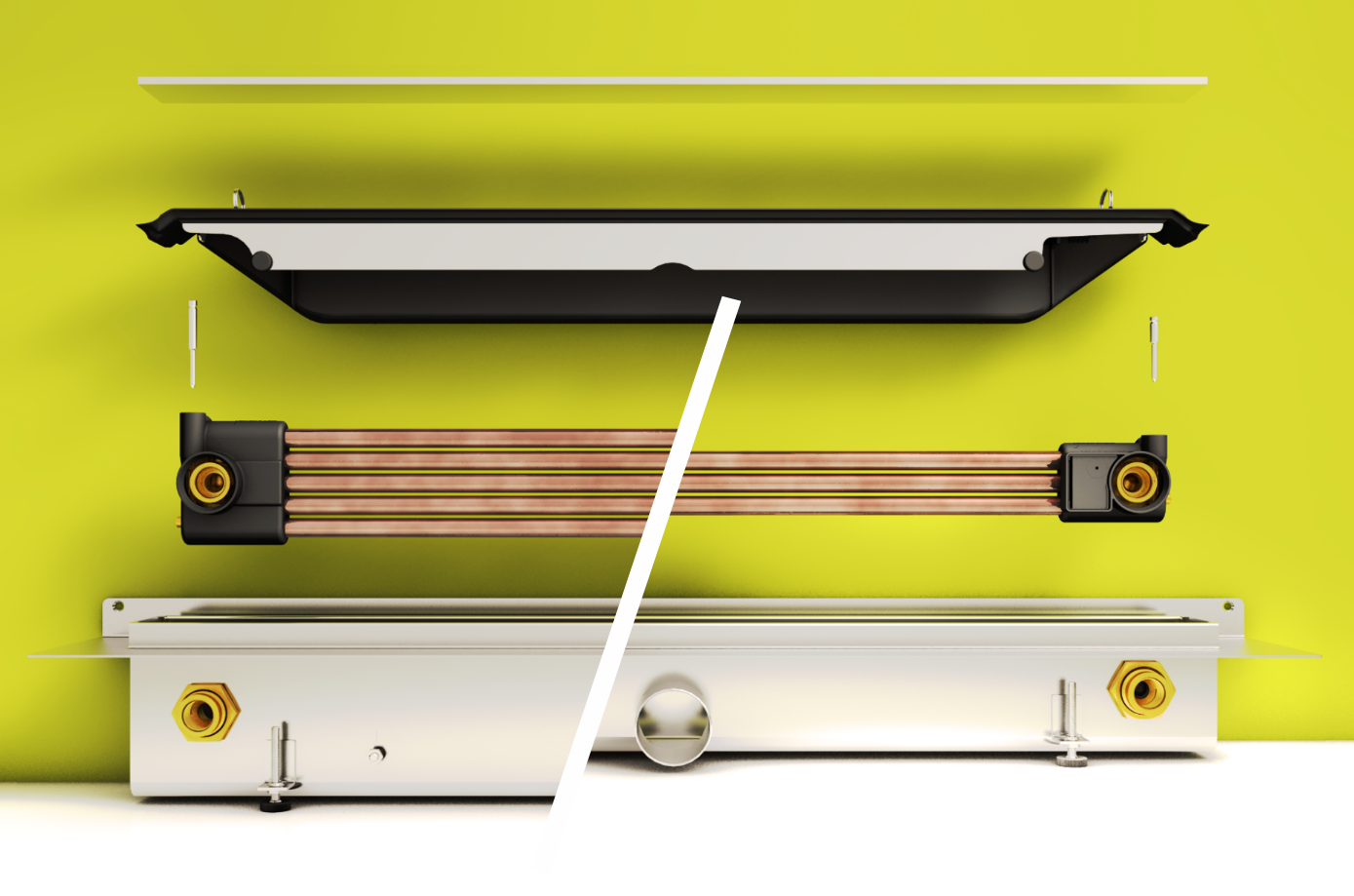
Shower with heat recycling
Abstract Why waste water heat recovery? Thanks to ever stricter regulations on the building envelope and consequently thicker insulation, energy consumption for heating has been massively reduced over the past decades. However, the energy requirement for hot water remains constant. Due to the increased hygiene requirements and ever larger overhead showers, it can even be assumed that the energy consumption for hot water – and especially for showers – will increase even more. Nowadays a household needs the same amount of energy for hot water as for the entire space heating system. Time to “plug” the last big hole in the insulation. Because it really makes no sense to produce a lot of hot water with valuable energy, which we dispose of after only two seconds of use. Videos : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I_9H0Qqn7as https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h_ToEu6udik https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yn9PqkblnvA https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z3MP5ARX76w Author: Schmid, Reto.
Abstract Why waste water heat recovery? Thanks to ever stricter regulations on the building envelope and consequently thicker insulation, energy consumption for heating has been massively reduced over the past decades. However, the energy requirement for hot water remains constant. Due to the increased hygiene requirements and ever larger overhead showers, it can even be assumed that the energy consumption for hot water – and especially for showers – will increase even more. Nowadays a household needs the same amount of energy for hot water as for the entire space heating system. Time to “plug” the last big hole in the insulation. Because it really makes no sense to produce a lot of hot water with valuable energy, which we dispose of after only two seconds of use. Videos : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I_9H0Qqn7as https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h_ToEu6udik https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yn9PqkblnvA https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z3MP5ARX76w Author: Schmid, Reto.
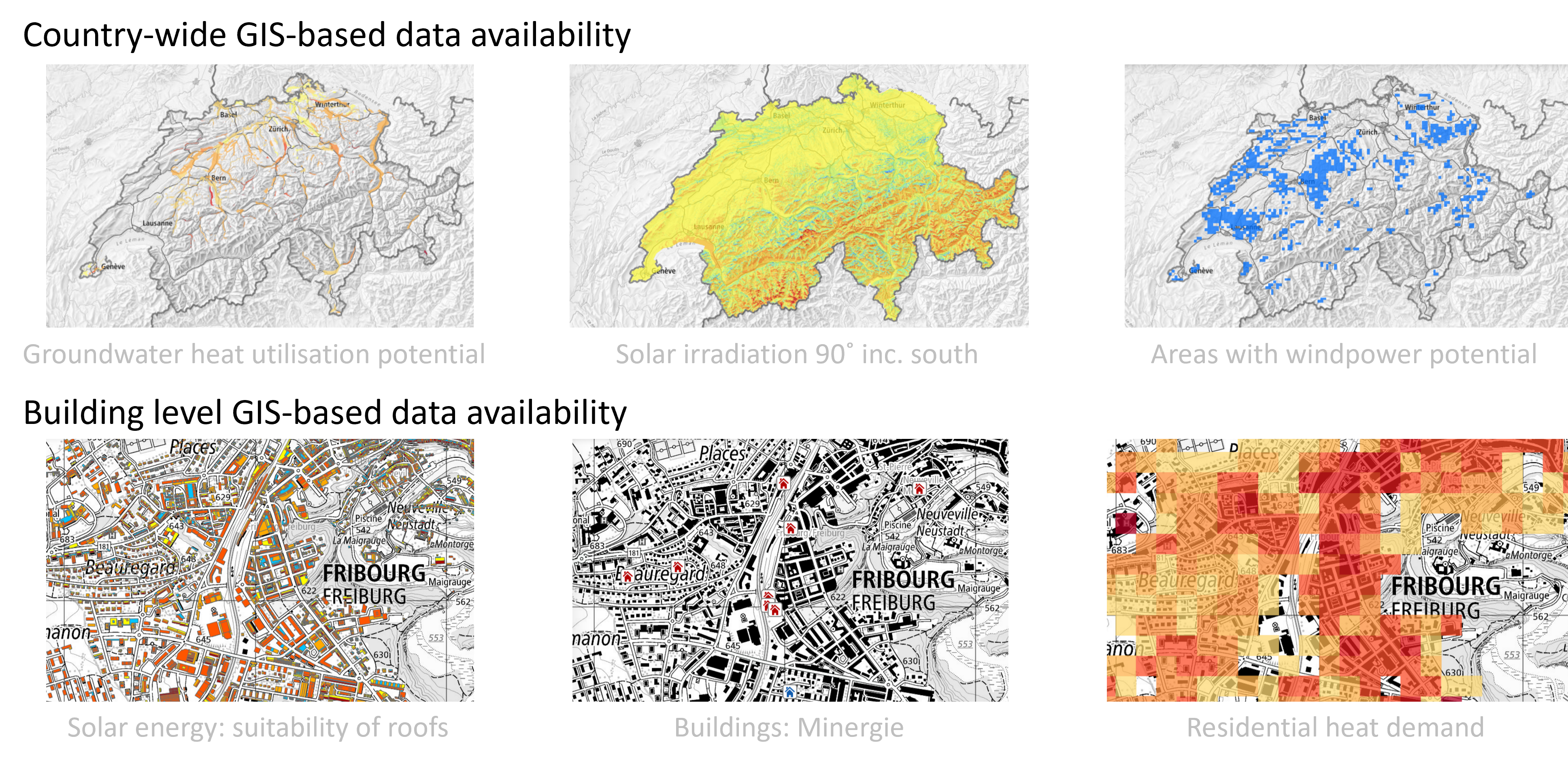
White paper on GIS- and data-driven tools for identifying and planning energy efficient building renovations in Switzerland
Abstract This white paper examines the current status and potential of GIS- and data-driven tools in supporting energy-efficient building renovations in Switzerland. Heating remains a dominant component of the country’s energy demand, and upgrading the existing building stock is critical to achieving the 2050 net-zero targets. While numerous digital tools exist to aid planning, their effectiveness is limited by inconsistent, incomplete, and inaccessible building data across cantons and municipalities. Through a case study in the municipality of Stäfa, we illustrate how disparate data sources produce widely varying results, even for fundamental parameters such as energy reference area and heat demand. The paper highlights the importance of accurate, harmonized, and openly accessible data, ideally integrated into a GIS-based framework. Key recommendations include the need for coordinated national strategies for data collection and standardization, improved legal frameworks for open energy data, and the development of modular, user-oriented tools to support stakeholders in renovation decision-making. Authors: Kelevitz, Krisztina ; Philippen, Daniel.
Abstract This white paper examines the current status and potential of GIS- and data-driven tools in supporting energy-efficient building renovations in Switzerland. Heating remains a dominant component of the country’s energy demand, and upgrading the existing building stock is critical to achieving the 2050 net-zero targets. While numerous digital tools exist to aid planning, their effectiveness is limited by inconsistent, incomplete, and inaccessible building data across cantons and municipalities. Through a case study in the municipality of Stäfa, we illustrate how disparate data sources produce widely varying results, even for fundamental parameters such as energy reference area and heat demand. The paper highlights the importance of accurate, harmonized, and openly accessible data, ideally integrated into a GIS-based framework. Key recommendations include the need for coordinated national strategies for data collection and standardization, improved legal frameworks for open energy data, and the development of modular, user-oriented tools to support stakeholders in renovation decision-making. Authors: Kelevitz, Krisztina ; Philippen, Daniel.

FACTSHEETS ON HEAT PUMP SOLUTIONS FOR EXISTING BUILDINGS
ABSTRACT Five real and archetypal buildings across Switzerland have been selected and analyzed with the goal to compare different heat pump-based solutions for the replacement of fossil heating system. With the collaboration of implementation partner Scheco AG, the results have been summarized in factsheets. The factsheets can help building owners, planners, and public authorities with the selection of variants. ZUSAMMENFASSUNG Fünf reale und archetypische Gebäude in der Schweiz wurden ausgewählt und analysiert, um verschiedene Wärmepumpenlösungen für den Ersatz fossiler Heizungssysteme zu vergleichen. In Zusammenarbeit mit dem Umsetzungspartner Scheco AG wurden die Ergebnisse in Factsheets zusammengefasst. Die Factsheets können Gebäudeeigentümern, Planern und Behörden bei der Auswahl von Varianten unterstützen. RÉSUMÉ Cinq bâtiments existants, archétypes de la Suisse, ont été sélectionnés et analysés dans le but de comparer différentes solutions basées sur des pompes à chaleur pour le remplacement des systèmes de chauffage fossiles. En collaboration avec le partenaire de mise en œuvre Scheco AG, les résultats ont été résumés dans des fiches d'information. Ces fiches peuvent aider les propriétaires de bâtiments, les planificateurs et les autorités publiques à choisir parmi les différentes options. SOMMARIO Cinque edifici reali e archetipici in tutta la Svizzera sono stati selezionati e analizzati con l'obiettivo di confrontare diverse soluzioni basate su pompe di calore per la sostituzione dei sistemi di riscaldamento a combustibile fossile. In collaborazione con il partner di implementazione Scheco AG, i risultati sono stati riassunti in schede informative. Le schede informative possono aiutare i proprietari di edifici, i progettisti e le autorità pubbliche nella scelta delle varianti di riscaldamento. Project partners: SPF, Scheco AG. Authors: Calabrese, Toni; Philippen, Daniel; Löhrer, Rolf.
ABSTRACT Five real and archetypal buildings across Switzerland have been selected and analyzed with the goal to compare different heat pump-based solutions for the replacement of fossil heating system. With the collaboration of implementation partner Scheco AG, the results have been summarized in factsheets. The factsheets can help building owners, planners, and public authorities with the selection of variants. ZUSAMMENFASSUNG Fünf reale und archetypische Gebäude in der Schweiz wurden ausgewählt und analysiert, um verschiedene Wärmepumpenlösungen für den Ersatz fossiler Heizungssysteme zu vergleichen. In Zusammenarbeit mit dem Umsetzungspartner Scheco AG wurden die Ergebnisse in Factsheets zusammengefasst. Die Factsheets können Gebäudeeigentümern, Planern und Behörden bei der Auswahl von Varianten unterstützen. RÉSUMÉ Cinq bâtiments existants, archétypes de la Suisse, ont été sélectionnés et analysés dans le but de comparer différentes solutions basées sur des pompes à chaleur pour le remplacement des systèmes de chauffage fossiles. En collaboration avec le partenaire de mise en œuvre Scheco AG, les résultats ont été résumés dans des fiches d'information. Ces fiches peuvent aider les propriétaires de bâtiments, les planificateurs et les autorités publiques à choisir parmi les différentes options. SOMMARIO Cinque edifici reali e archetipici in tutta la Svizzera sono stati selezionati e analizzati con l'obiettivo di confrontare diverse soluzioni basate su pompe di calore per la sostituzione dei sistemi di riscaldamento a combustibile fossile. In collaborazione con il partner di implementazione Scheco AG, i risultati sono stati riassunti in schede informative. Le schede informative possono aiutare i proprietari di edifici, i progettisti e le autorità pubbliche nella scelta delle varianti di riscaldamento. Project partners: SPF, Scheco AG. Authors: Calabrese, Toni; Philippen, Daniel; Löhrer, Rolf.

Policies for accelerating fossil heating systems replacement and building renovation
Abstract This policy analysis covers three key pieces of Swiss regulation related to heating system replacements: the Gebäudeprogramm subsidy scheme, the Federal Model Provisions of the Cantons (MuKEn2014), and complementary measures by the Cantons, including oil and gas heating bans. By analysing those regulations and comparing renovation and heating system replacement trends among the cantons, we identify common patterns, key barriers and success factors to inform policy of how to accelerate heating system replacement and renovation. Our analysis shows that the Swiss policy approach based on a combination of ambitious renovation standards (sticks) and subsidies for energy-efficient renovations (carrots) is generally working. However, it should be strengthened and improved to increase its effectiveness. One critical improvement is an increased harmonisation of standards among the cantons. Despite efforts for harmonisation and coordination through the Model Provisions of the Cantons (MuKEn), regulations for heating system replacements and subsidies are still fragmented. For instance, MuKEn2014 asks for a 10% minimum share of renewable energy in new heating installations, but the cantons have implemented minimum shares varying from 10% to 100%. Our analysis also shows that there is large potential for peer-to-peer learning among the cantons to increase the effectiveness of the policy instruments related to renovation and heating systems replacement, considering that there is large variability in performance /efficiency indicators such as: the speed of heating system replacements, a combination with deeper building renovation measures, or the amount of private capital leveraged by the subsidies. Some of these differences can be explained by structural differences among cantons (e.g., existing building stock, socio-economic realities and administrative capacities), but local implementation strategies also play a role. We conclude that the policy approach to fossil heating replacements and energy efficiency renovations in Switzerland is working overall. It should be strengthened and improved instead of being scaled down. In our report, we provide concrete recommendations for policies and measures, as well as desirable design features, to improve the implementation of existing and forthcoming policies, like the MuKEn2025 guidelines, to support political decisions to accelerate the necessary transformation. Authors: Yanguas Parra, Paola Andrea; Markard, Jochen.
Abstract This policy analysis covers three key pieces of Swiss regulation related to heating system replacements: the Gebäudeprogramm subsidy scheme, the Federal Model Provisions of the Cantons (MuKEn2014), and complementary measures by the Cantons, including oil and gas heating bans. By analysing those regulations and comparing renovation and heating system replacement trends among the cantons, we identify common patterns, key barriers and success factors to inform policy of how to accelerate heating system replacement and renovation. Our analysis shows that the Swiss policy approach based on a combination of ambitious renovation standards (sticks) and subsidies for energy-efficient renovations (carrots) is generally working. However, it should be strengthened and improved to increase its effectiveness. One critical improvement is an increased harmonisation of standards among the cantons. Despite efforts for harmonisation and coordination through the Model Provisions of the Cantons (MuKEn), regulations for heating system replacements and subsidies are still fragmented. For instance, MuKEn2014 asks for a 10% minimum share of renewable energy in new heating installations, but the cantons have implemented minimum shares varying from 10% to 100%. Our analysis also shows that there is large potential for peer-to-peer learning among the cantons to increase the effectiveness of the policy instruments related to renovation and heating systems replacement, considering that there is large variability in performance /efficiency indicators such as: the speed of heating system replacements, a combination with deeper building renovation measures, or the amount of private capital leveraged by the subsidies. Some of these differences can be explained by structural differences among cantons (e.g., existing building stock, socio-economic realities and administrative capacities), but local implementation strategies also play a role. We conclude that the policy approach to fossil heating replacements and energy efficiency renovations in Switzerland is working overall. It should be strengthened and improved instead of being scaled down. In our report, we provide concrete recommendations for policies and measures, as well as desirable design features, to improve the implementation of existing and forthcoming policies, like the MuKEn2025 guidelines, to support political decisions to accelerate the necessary transformation. Authors: Yanguas Parra, Paola Andrea; Markard, Jochen.
RENOWAVE COACHING TOOLS - TOOLBOX
Abstract This TOOLBOX offers Swiss municipalities, energy renovation stakeholders and property owners a variety of open-source tools. It contains tools developed within the Renowave project, as well as additional information, providing a comprehensive selection of resources. Municipalities can use the tools to analyze, define and implement their strategy, guiding building owners towards ambitious goals and supporting them throughout their projects until renovation is complete. This encourages the energy-efficient renovation of private housing within municipalities and, consequently, across Switzerland. All tools are free and open source. No user information is stored. Links: https://renowave-coachingtools.ch/de/index https://renowave-coachingtools.ch/fr/index Authors: Institut inPACT - Energie Climat Environnement Architecture
Abstract This TOOLBOX offers Swiss municipalities, energy renovation stakeholders and property owners a variety of open-source tools. It contains tools developed within the Renowave project, as well as additional information, providing a comprehensive selection of resources. Municipalities can use the tools to analyze, define and implement their strategy, guiding building owners towards ambitious goals and supporting them throughout their projects until renovation is complete. This encourages the energy-efficient renovation of private housing within municipalities and, consequently, across Switzerland. All tools are free and open source. No user information is stored. Links: https://renowave-coachingtools.ch/de/index https://renowave-coachingtools.ch/fr/index Authors: Institut inPACT - Energie Climat Environnement Architecture
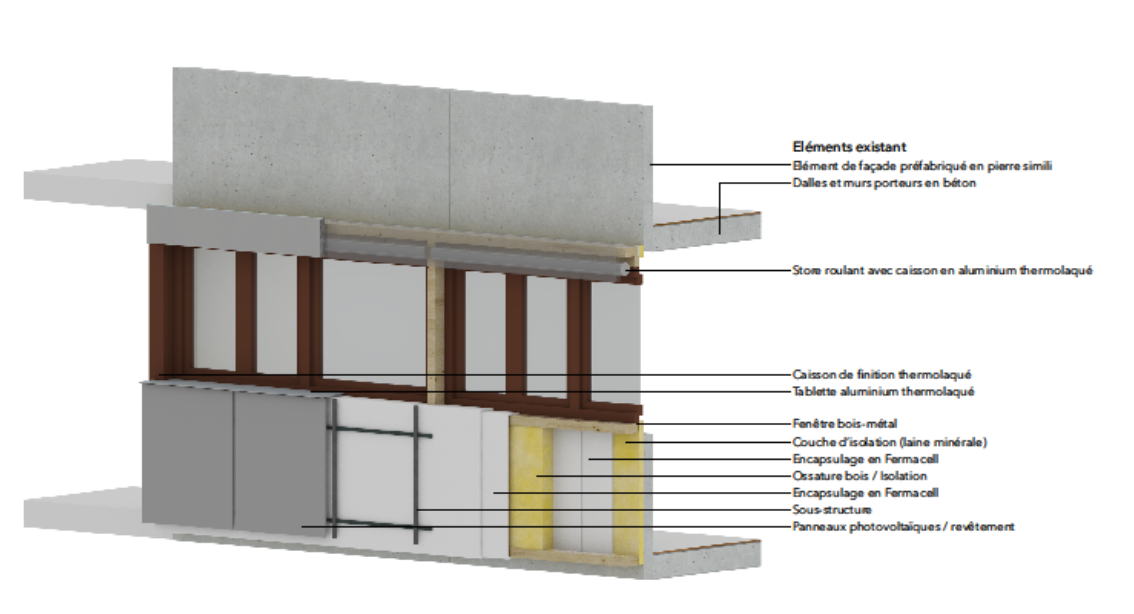
Feasibility study for the renovation of a post-war high-rise building in Lancy (Geneva)
Abstract The University of Applied Science OST and its partners of the Renowave subproject 2.3 have developed a renovation concept whereby new prefabricated façade elements are applied to the exterior of existing walls of buildings in need of refurbishment. These elements provide not only insulation but also play a role in the production and distribution of energy. The town of Lancy, a Renowave implementation partner, suggested using a 1963 high-rise building as a pilot project to test the innovative solution of the so called “Prosumer Skin active façade kits”. The present report has been redacted by HEPIA and was presented to the municipality as a feasibility study. It includes an analysis of the existing structure and technical installations of the building, an assessment of the current local and federal regulations and a recommended renovation strategy. Based on the thermal calculations (OST), the composition of the prefabricated façade elements was determined, as well as the inclusion of solar panels for electricity production. Heat pump solutions for the heating system were studied by the partners of subproject 2.3. However, the imminent arrival of the town heating led to the elimination of these solutions, resulting in the removal of the heating component from the proposed prefabricated façade element. Nevertheless, the renovation strategy has been discussed with the authorities, and the results of these consultations are listed in the report. Furthermore, the efficiency of a solar installations on the roof and the façade has been evaluated, and a cost estimate for the renovation completes the feasibility study. Authors: Rinquet, Lionel ; Fowler, Grit.
Abstract The University of Applied Science OST and its partners of the Renowave subproject 2.3 have developed a renovation concept whereby new prefabricated façade elements are applied to the exterior of existing walls of buildings in need of refurbishment. These elements provide not only insulation but also play a role in the production and distribution of energy. The town of Lancy, a Renowave implementation partner, suggested using a 1963 high-rise building as a pilot project to test the innovative solution of the so called “Prosumer Skin active façade kits”. The present report has been redacted by HEPIA and was presented to the municipality as a feasibility study. It includes an analysis of the existing structure and technical installations of the building, an assessment of the current local and federal regulations and a recommended renovation strategy. Based on the thermal calculations (OST), the composition of the prefabricated façade elements was determined, as well as the inclusion of solar panels for electricity production. Heat pump solutions for the heating system were studied by the partners of subproject 2.3. However, the imminent arrival of the town heating led to the elimination of these solutions, resulting in the removal of the heating component from the proposed prefabricated façade element. Nevertheless, the renovation strategy has been discussed with the authorities, and the results of these consultations are listed in the report. Furthermore, the efficiency of a solar installations on the roof and the façade has been evaluated, and a cost estimate for the renovation completes the feasibility study. Authors: Rinquet, Lionel ; Fowler, Grit.
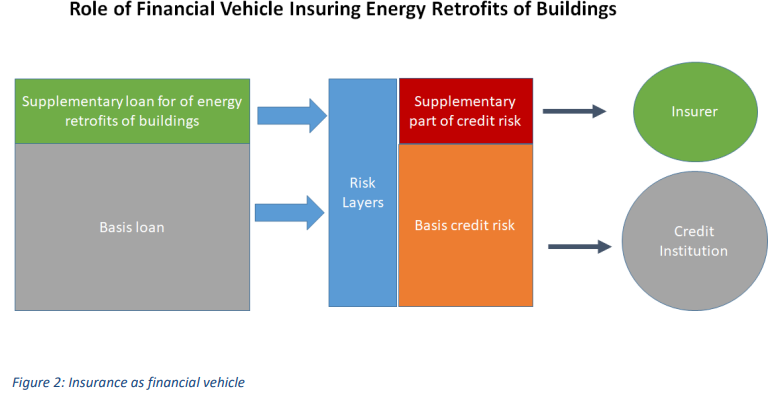
Credit Risk of Financial Vehicle for Energy Retrofits of Buildings (RENOWAVE 3.1)
Abstract Cost of capital represents an important component of the mortgage rate. The impact of risk sharing approach depends on the benefits of credit institutions and the price of shared risk. The aim of this paper is to prove that the required capital of an insuring vehicle is low enough to allow acceptable insurance premium that might accelerate noteworthy market demand for sustainable renovations/investments of real estates. For this purpose, we will define model points representing risk classes and measure the required capital based on major risk metrics and compare them with the existing standard regulations in absence of the suggested regulation. Authors: Drometer, Marcus et al.
Abstract Cost of capital represents an important component of the mortgage rate. The impact of risk sharing approach depends on the benefits of credit institutions and the price of shared risk. The aim of this paper is to prove that the required capital of an insuring vehicle is low enough to allow acceptable insurance premium that might accelerate noteworthy market demand for sustainable renovations/investments of real estates. For this purpose, we will define model points representing risk classes and measure the required capital based on major risk metrics and compare them with the existing standard regulations in absence of the suggested regulation. Authors: Drometer, Marcus et al.
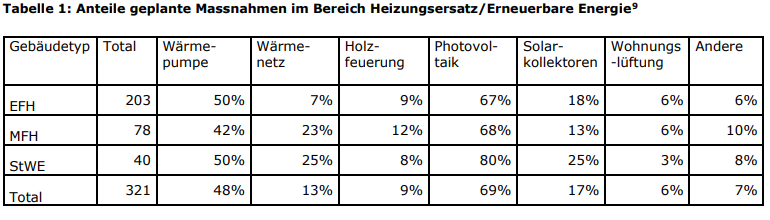
Herausforderungen bei energetischen Sanierungen: Welche Rolle spielt die Finanzierung?
Abstract Im Rahmen des RENOWAVE Projekts, das von der Schweizerischen Agentur für Innovationsförderung (Innosuisse) unterstützt wird, hat die Hochschule Luzern eine Befragung durchgeführt, um die Herausforderungen, denen sich Hauseigentümer/-innen bei der Finanzierung von energetischen Sanierungen gegenübersehen, besser zu verstehen. Die vorliegende Befragung zeigt, dass grundsätzlich eine hohe Bereitschaft für die Realisierung energetischer Massnahmen vorhanden ist. Darüber hinaus sind die Präferenzen der Hauseigentümer/-innen, welche Massnahmen realisieren möchten, langfristig ausgerichtet. Insgesamt gibt es Hinweise darauf, dass trotz Förderung die Finanzierung ein massgebliches Hindernis bei der Realisierung geplanter energetischer Massnahmen darstellt. Rund die Hälfte derjenigen, die sich bereits konkret um die Finanzierung einer geplanten Massnahme gekümmert haben, ist auf fremde Mittel angewiesen. Des Weiteren gibt ebenfalls rund die Hälfte der Befragte an, dass ein besserer Zugang zu Finanzierung ihre Entscheidung stark beeinflussen würde. Bei der Interpretation der Ergebnisse muss jedoch beachtet werden, dass die beobachtete Stichprobe an Hauseigentümern/-innen aufgrund von Selektionsproblemen nicht voll repräsentativ sein dürfte. Authors: Drometer, Marcus ; Gallati, Justus ; Habermacher, Florian ; King, Marvin ; Zimmermann, Yvonne Seiler ; Zöllner, Silke.
Abstract Im Rahmen des RENOWAVE Projekts, das von der Schweizerischen Agentur für Innovationsförderung (Innosuisse) unterstützt wird, hat die Hochschule Luzern eine Befragung durchgeführt, um die Herausforderungen, denen sich Hauseigentümer/-innen bei der Finanzierung von energetischen Sanierungen gegenübersehen, besser zu verstehen. Die vorliegende Befragung zeigt, dass grundsätzlich eine hohe Bereitschaft für die Realisierung energetischer Massnahmen vorhanden ist. Darüber hinaus sind die Präferenzen der Hauseigentümer/-innen, welche Massnahmen realisieren möchten, langfristig ausgerichtet. Insgesamt gibt es Hinweise darauf, dass trotz Förderung die Finanzierung ein massgebliches Hindernis bei der Realisierung geplanter energetischer Massnahmen darstellt. Rund die Hälfte derjenigen, die sich bereits konkret um die Finanzierung einer geplanten Massnahme gekümmert haben, ist auf fremde Mittel angewiesen. Des Weiteren gibt ebenfalls rund die Hälfte der Befragte an, dass ein besserer Zugang zu Finanzierung ihre Entscheidung stark beeinflussen würde. Bei der Interpretation der Ergebnisse muss jedoch beachtet werden, dass die beobachtete Stichprobe an Hauseigentümern/-innen aufgrund von Selektionsproblemen nicht voll repräsentativ sein dürfte. Authors: Drometer, Marcus ; Gallati, Justus ; Habermacher, Florian ; King, Marvin ; Zimmermann, Yvonne Seiler ; Zöllner, Silke.

Investitions- und Strategierechner (ISR) light
Abstract Goal/purpose: With the help of the Investment and Strategy Calculator (ISR) light tool, real estate project developers can quickly (in approx. 2-3 hours) obtain an overview of their project development. The guide and the Excel-based tool are designed to help builders define and structure their project development. The guide is designed to guide them through important questions in project development and includes five case studies on renovations. The investment strategy calculator focuses on existing properties. The core of the tool is the inventory. Limitation/delimitation: Residential properties in the city of Zurich (beta version). The copyright for the investment strategy calculator is held by Matthias Catto (matthias@catto.ch). If you have any questions or suggestions, please feel free to contact him. Ziel/Zweck: Mit Hilfe des Investitions- und Strategierechner (ISR) light Tools erhalten Immobilienprojektentwickler/-innen in kurzer Zeit (ca. 2-3 h) einen Überblick zu ihrer Projektentwicklung. Der Leitfaden und das auf Excel basierte Tool helfen dem Bauherrn, die Projektentwicklung zu definieren und zu strukturieren. Der Leitfaden führt hierbei durch wichtige Fragestellungen in der Projektentwicklung und beinhaltet fünf Fallbeispiele zu Sanierungen. Der Investitions- und Strategierechner (ISR) light fokussiert auf Bestandsliegenschaften. Kern des Tools ist die Bestandsaufnahme. Limitierung/Abgrenzung: Wohnliegenschaften in der Stadt Zürich (Beta-Version). Die Urheberrechte des Investitions- und Strategierechner (ISR) light liegen bei Matthias Catto (matthias@catto.ch). Bei Fragen oder Anregungen können Sie sich gerne bei ihm melden. Authors: Catto, Matthias (PwC); Kraft, Christian (HSLU); Bittel, Michel (HSLU); Kempf, Constantin (HSLU).
Abstract Goal/purpose: With the help of the Investment and Strategy Calculator (ISR) light tool, real estate project developers can quickly (in approx. 2-3 hours) obtain an overview of their project development. The guide and the Excel-based tool are designed to help builders define and structure their project development. The guide is designed to guide them through important questions in project development and includes five case studies on renovations. The investment strategy calculator focuses on existing properties. The core of the tool is the inventory. Limitation/delimitation: Residential properties in the city of Zurich (beta version). The copyright for the investment strategy calculator is held by Matthias Catto (matthias@catto.ch). If you have any questions or suggestions, please feel free to contact him. Ziel/Zweck: Mit Hilfe des Investitions- und Strategierechner (ISR) light Tools erhalten Immobilienprojektentwickler/-innen in kurzer Zeit (ca. 2-3 h) einen Überblick zu ihrer Projektentwicklung. Der Leitfaden und das auf Excel basierte Tool helfen dem Bauherrn, die Projektentwicklung zu definieren und zu strukturieren. Der Leitfaden führt hierbei durch wichtige Fragestellungen in der Projektentwicklung und beinhaltet fünf Fallbeispiele zu Sanierungen. Der Investitions- und Strategierechner (ISR) light fokussiert auf Bestandsliegenschaften. Kern des Tools ist die Bestandsaufnahme. Limitierung/Abgrenzung: Wohnliegenschaften in der Stadt Zürich (Beta-Version). Die Urheberrechte des Investitions- und Strategierechner (ISR) light liegen bei Matthias Catto (matthias@catto.ch). Bei Fragen oder Anregungen können Sie sich gerne bei ihm melden. Authors: Catto, Matthias (PwC); Kraft, Christian (HSLU); Bittel, Michel (HSLU); Kempf, Constantin (HSLU).
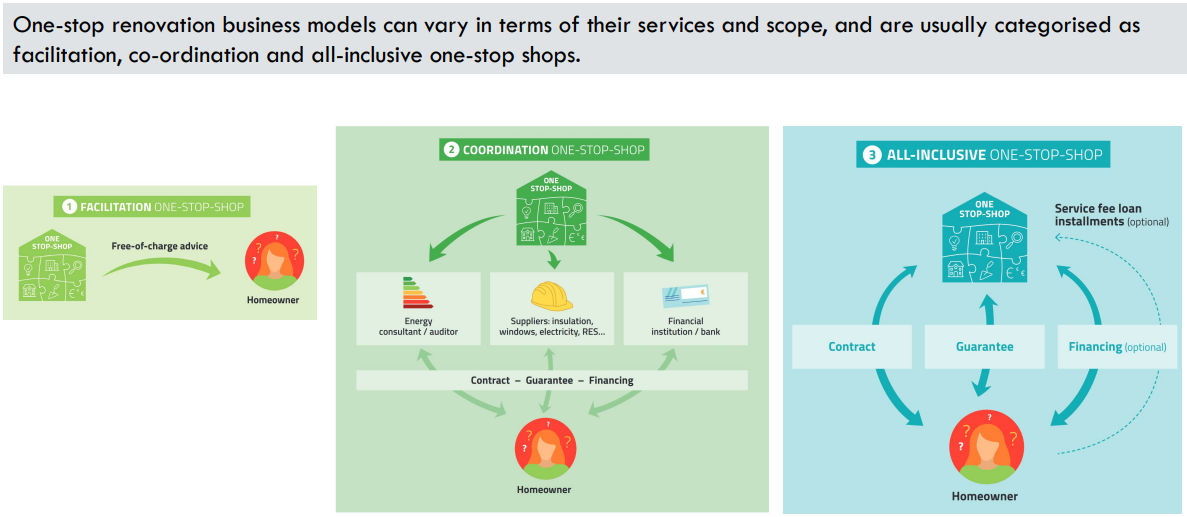
One Stop Shop Guidelines
Abstract A One-Stop Shop (OSS) for renovation is a centralized service model that simplifies the renovation process by providing homeowners and building owners with guidance, resources, and support throughout their project. Designing an OSS in a participatory manner ensures that it addresses the specific needs of a region while fostering ownership and commitment among local actors. This guideline is designed for organizations interested in coordinating OSS business models. It includes useful workshop materials, offering ideas for planning and implementing stakeholder engagement activities. Additionally, it presents valuable insights from previous workshops that serve as examples and inspiration for other communities. These insights showcase best practices and creative approaches to foster collaboration and innovation. Authors: Zapata, Juliana; Haase, Matthias; Kauz, Christoph; Schmid, Christian; Bätschmann, Marc; Peran, David; Ulli-Beer, Silvia.
Abstract A One-Stop Shop (OSS) for renovation is a centralized service model that simplifies the renovation process by providing homeowners and building owners with guidance, resources, and support throughout their project. Designing an OSS in a participatory manner ensures that it addresses the specific needs of a region while fostering ownership and commitment among local actors. This guideline is designed for organizations interested in coordinating OSS business models. It includes useful workshop materials, offering ideas for planning and implementing stakeholder engagement activities. Additionally, it presents valuable insights from previous workshops that serve as examples and inspiration for other communities. These insights showcase best practices and creative approaches to foster collaboration and innovation. Authors: Zapata, Juliana; Haase, Matthias; Kauz, Christoph; Schmid, Christian; Bätschmann, Marc; Peran, David; Ulli-Beer, Silvia.

Komfortfaktoren bei Sanierungen - ein Überblick
Abstract DE: Der übersichtliche Flyer wurde in Zusammenarbeit mit Casafair erstellt, um sowohl Mieter:innen als auch Eigentümer:innen für die behaglichen Aspekte von Sanierungen zu sensibilisieren. Ziel ist es, auf die Bedeutung qualitativer Kriterien bei Sanierungen aufmerksam zu machen und aufzuzeigen, dass Sanierungen auch subtilere, aber wirkungsvolle Qualitäten mit sich bringen können. EN: The flyer was created in collaboration with Casafair to draw the attention of tenants and owners alike to the comfort aspects of renovations. The aim is to raise awareness of the issue of quality criteria in renovations and to show that renovation can bring additional, more subtle qualities. Authors: Brigger, Sabine; King, Marvin; Huber, Daniel.
Abstract DE: Der übersichtliche Flyer wurde in Zusammenarbeit mit Casafair erstellt, um sowohl Mieter:innen als auch Eigentümer:innen für die behaglichen Aspekte von Sanierungen zu sensibilisieren. Ziel ist es, auf die Bedeutung qualitativer Kriterien bei Sanierungen aufmerksam zu machen und aufzuzeigen, dass Sanierungen auch subtilere, aber wirkungsvolle Qualitäten mit sich bringen können. EN: The flyer was created in collaboration with Casafair to draw the attention of tenants and owners alike to the comfort aspects of renovations. The aim is to raise awareness of the issue of quality criteria in renovations and to show that renovation can bring additional, more subtle qualities. Authors: Brigger, Sabine; King, Marvin; Huber, Daniel.
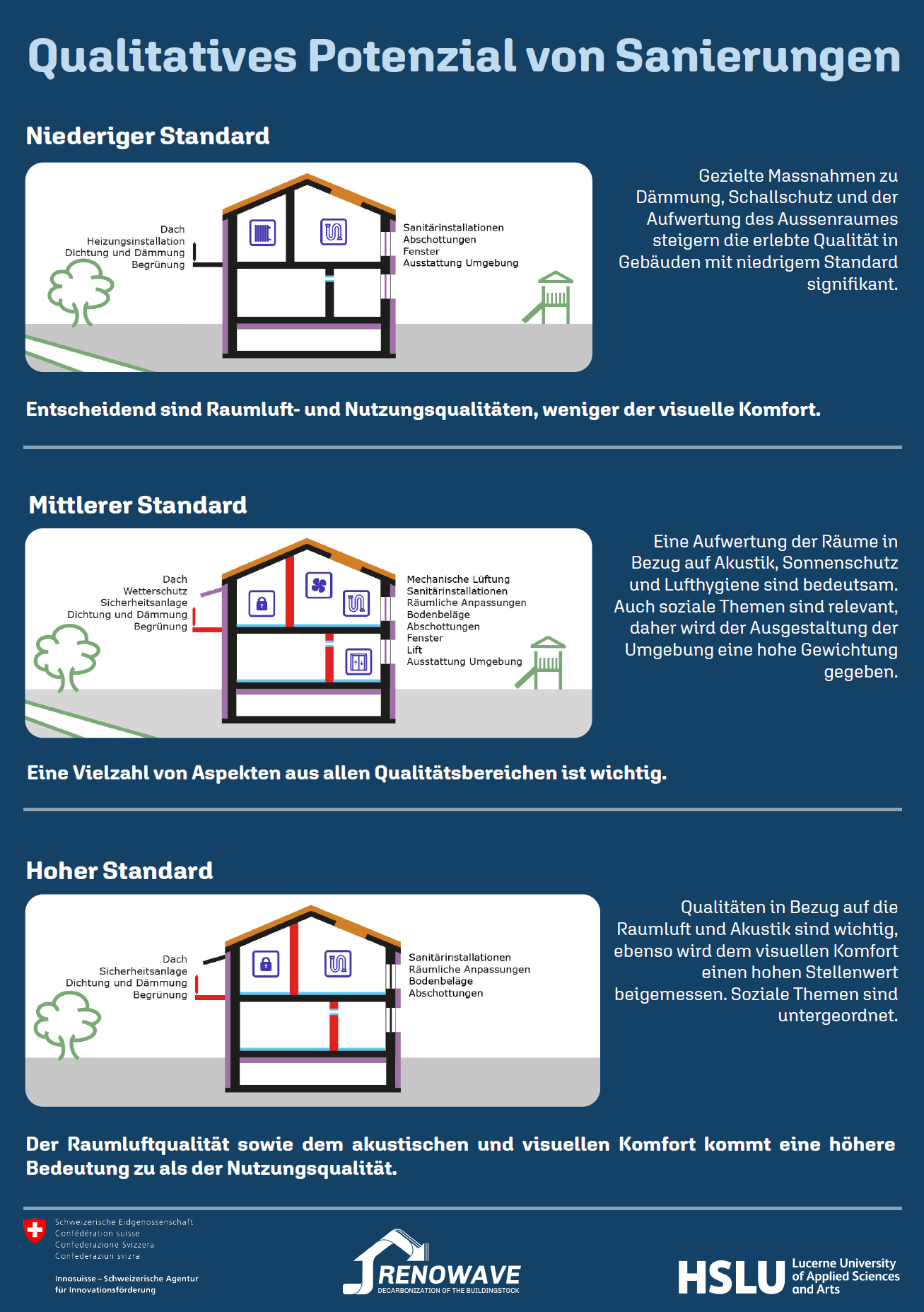
Sanierungsmassnahmen und ihr qualitativer Nutzen je nach Standard - eine Übersicht
Abstract DE: Dieses Dokument fasst die Resultate der Forschungsarbeit grafisch zusammen. Auf einfache Weise ist erkennbar, welche Sanierungsmassnahmen für verschiedene Standards den grössten Nutzen bringen. So lassen sich gezielt jene Massnahmen umsetzen, die für den jeweiligen Standard den grössten Mehrwert im Hinblick auf qualitative Verbesserungen bieten. EN: This document summarizes the results of the research work in graphical form. It is easy to see which renovation measures bring the greatest benefits for different standards. This allows targeted implementation of measures that bring the greatest added value in terms of quality improvements for the standard in question. Authors: Brigger, Sabine; King, Marvin.
Abstract DE: Dieses Dokument fasst die Resultate der Forschungsarbeit grafisch zusammen. Auf einfache Weise ist erkennbar, welche Sanierungsmassnahmen für verschiedene Standards den grössten Nutzen bringen. So lassen sich gezielt jene Massnahmen umsetzen, die für den jeweiligen Standard den grössten Mehrwert im Hinblick auf qualitative Verbesserungen bieten. EN: This document summarizes the results of the research work in graphical form. It is easy to see which renovation measures bring the greatest benefits for different standards. This allows targeted implementation of measures that bring the greatest added value in terms of quality improvements for the standard in question. Authors: Brigger, Sabine; King, Marvin.
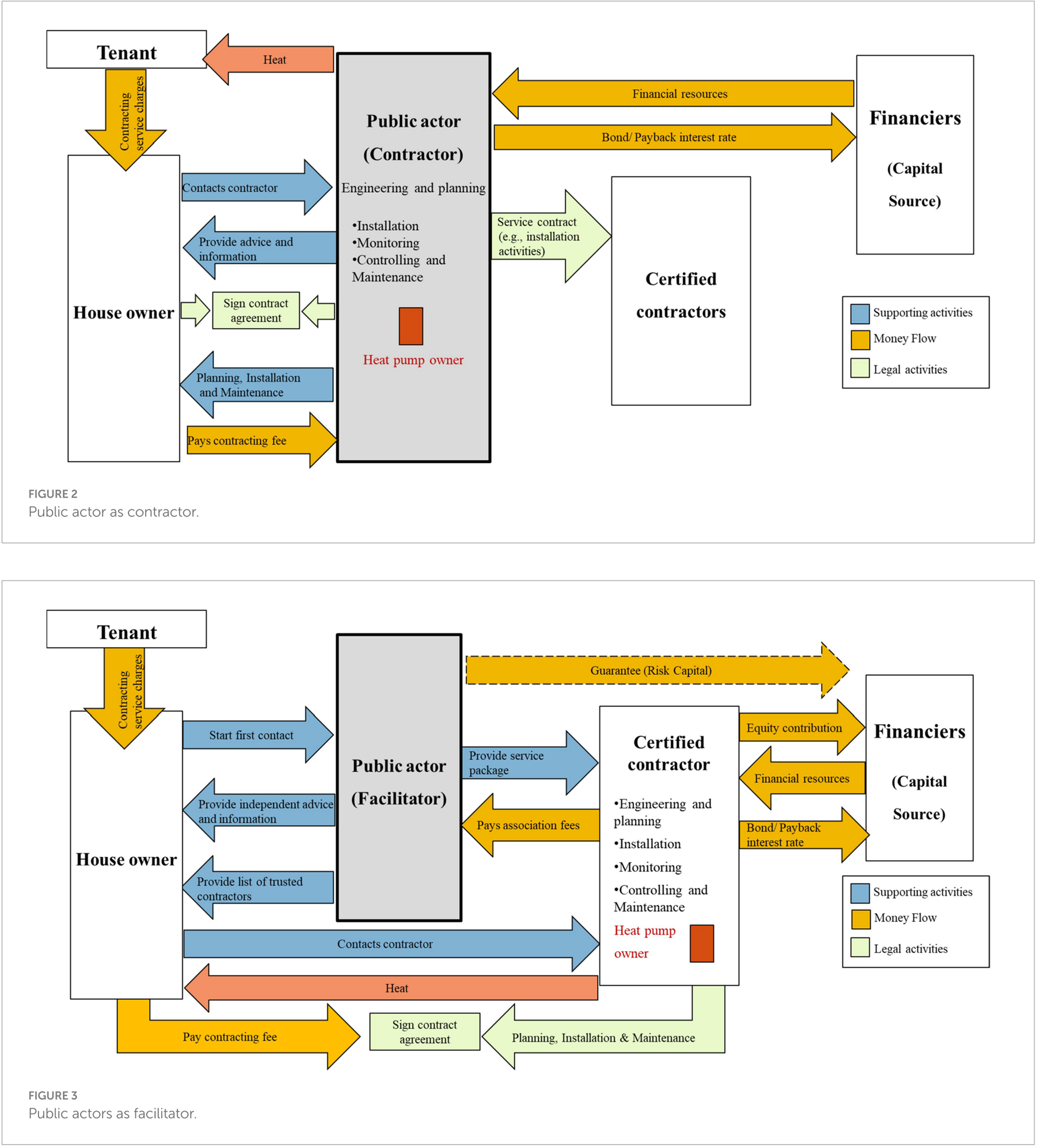
Mitigating risks and breaking barriers, energy supply contracting in multifamily houses: an ecosystem perspective
Abstract Introduction: In Switzerland, heating accounts for 70% of a building’s energy consumption, mostly fueled by fossil sources. Recently, cantonal regulations have mandated the use of renewable energy in heating, making heat pumps more significant. This study examines how public and private actors can create or transform a business ecosystem to facilitate heat pump adoption in multi-family houses and which business models, resources, and activities are most effective to support this transformation. Methods: We conducted a literature review and 13 semi-structured interviews with experts in heat pumps and contracting business models. The interviews were analyzed using an ecosystem framework. Results: Our findings revealed three primary barriers to the adoption of heat pumps in MFHs: technical challenges, lack of expertise, and regulatory issues. In terms of contracting business models, high transaction costs and customer acceptance are significant obstacles. Additionally, we discovered that in Switzerland, contracting is predominantly offered by public-oriented organizations with ready access to capital. Discussion: The study emphasizes the necessity for collaboration among various actors to facilitate the implementation of contracting solutions with the goal of accelerating the adoption of heat pumps in multifamily housing. Key activities include generating the necessary expertise and standardizing large heat pumps in MFHs, central government efforts to harmonize and facilitate HP regulations across cantons, as well as active communication and sensitization of building owners and users. Authors: Zapata, Juliana; Gallati, Justus; Ulli-Beer, Silvia.
Abstract Introduction: In Switzerland, heating accounts for 70% of a building’s energy consumption, mostly fueled by fossil sources. Recently, cantonal regulations have mandated the use of renewable energy in heating, making heat pumps more significant. This study examines how public and private actors can create or transform a business ecosystem to facilitate heat pump adoption in multi-family houses and which business models, resources, and activities are most effective to support this transformation. Methods: We conducted a literature review and 13 semi-structured interviews with experts in heat pumps and contracting business models. The interviews were analyzed using an ecosystem framework. Results: Our findings revealed three primary barriers to the adoption of heat pumps in MFHs: technical challenges, lack of expertise, and regulatory issues. In terms of contracting business models, high transaction costs and customer acceptance are significant obstacles. Additionally, we discovered that in Switzerland, contracting is predominantly offered by public-oriented organizations with ready access to capital. Discussion: The study emphasizes the necessity for collaboration among various actors to facilitate the implementation of contracting solutions with the goal of accelerating the adoption of heat pumps in multifamily housing. Key activities include generating the necessary expertise and standardizing large heat pumps in MFHs, central government efforts to harmonize and facilitate HP regulations across cantons, as well as active communication and sensitization of building owners and users. Authors: Zapata, Juliana; Gallati, Justus; Ulli-Beer, Silvia.

Qualitative Factors in Refurbishment - A New Evaluation Model for Strategic Priorization and Quality Improvements
EN: Owners, investors, and users are largely unaware that qualitative factors have a significant impact on long-term value retention. The project links qualitative aspects to the construction cost plan and highlights which renovation measures offer the greatest benefits for various standards. The evaluations enable renovation strategies to be specifically adapted and refined depending on the property standard. This allows investments to concentrate on those measures that generate the greatest qualitative added value for the respective standard. For tenants, this means that the qualities which actually influence their living situation, are improved; and for owners, that investments are made in a targeted manner. The analysis thus contributes to the further development of existing valuation approaches by highlighting qualitative factors as an integral part of renovation planning. ________________________________ DE: Qualitative Faktoren bei Sanierungen - Ein neues Bewertungsmodell zur strategischen Priorisierung und gezielten Qualitätssteigerung Eigentümer, Investoren und Nutzer sind sich oft nicht bewusst, dass qualitative Faktoren einen erheblichen Einfluss auf die langfristige Werterhaltung haben. Das Projekt verknüpft diese qualitativen Aspekte systematisch mit dem Baukostenplan (eBKP-H) und zeigt auf, welche baulichen Sanierungsmassnahmen je nach Objektstandard den grössten Nutzen stiften. Durch diese Auswertungen lassen sich Sanierungsstrategien gezielt an den jeweiligen Gebäudezustand anpassen und präzisieren. Investitionen können damit auf jene Massnahmen fokussiert werden, die für den jeweiligen Standard den grössten qualitativen Mehrwert erzeugen. Für die Mietenden bedeutet dies, dass jene Qualitäten verbessert werden, welche ihre Wohnsituation spürbar beeinflussen und für Eigentümerinnen und Eigentümer, dass ihre Investitionen zielgerichtet und wirkungsvoll eingesetzt werden. Damit leistet die Analyse einen Beitrag zur Weiterentwicklung bestehender Bewertungsansätze, indem sie qualitative Faktoren als integralen Bestandteil der strategischen Sanierungsplanung sichtbar und nutzbar macht.
EN: Owners, investors, and users are largely unaware that qualitative factors have a significant impact on long-term value retention. The project links qualitative aspects to the construction cost plan and highlights which renovation measures offer the greatest benefits for various standards. The evaluations enable renovation strategies to be specifically adapted and refined depending on the property standard. This allows investments to concentrate on those measures that generate the greatest qualitative added value for the respective standard. For tenants, this means that the qualities which actually influence their living situation, are improved; and for owners, that investments are made in a targeted manner. The analysis thus contributes to the further development of existing valuation approaches by highlighting qualitative factors as an integral part of renovation planning. ________________________________ DE: Qualitative Faktoren bei Sanierungen - Ein neues Bewertungsmodell zur strategischen Priorisierung und gezielten Qualitätssteigerung Eigentümer, Investoren und Nutzer sind sich oft nicht bewusst, dass qualitative Faktoren einen erheblichen Einfluss auf die langfristige Werterhaltung haben. Das Projekt verknüpft diese qualitativen Aspekte systematisch mit dem Baukostenplan (eBKP-H) und zeigt auf, welche baulichen Sanierungsmassnahmen je nach Objektstandard den grössten Nutzen stiften. Durch diese Auswertungen lassen sich Sanierungsstrategien gezielt an den jeweiligen Gebäudezustand anpassen und präzisieren. Investitionen können damit auf jene Massnahmen fokussiert werden, die für den jeweiligen Standard den grössten qualitativen Mehrwert erzeugen. Für die Mietenden bedeutet dies, dass jene Qualitäten verbessert werden, welche ihre Wohnsituation spürbar beeinflussen und für Eigentümerinnen und Eigentümer, dass ihre Investitionen zielgerichtet und wirkungsvoll eingesetzt werden. Damit leistet die Analyse einen Beitrag zur Weiterentwicklung bestehender Bewertungsansätze, indem sie qualitative Faktoren als integralen Bestandteil der strategischen Sanierungsplanung sichtbar und nutzbar macht.

Scalable PCM storage for renewable energy systems Compact Cell
Modular in use and with a small footprint, the scalable storage Compact Cell based on Phase Change Materials (PCM) offers maximum comfort in combination with heat pumps. Heat pumps are gaining ground worldwide. Our heat storages are designed to increase comfort in heat pump systems, reduce running times and facilitate implementation, in particular in retrofit application where space may be limited. Heat pumps extract energy from the environment and generate sustainable heat for heating and hot water. Electrically driven heat pumps generate 100% usable heat from around 20% electricity, thus conserving environmental resources. If the electricity is obtained from renewable sources, the environmental impact is further reduced. Heat pumps are versatile and are available in different configurations. By using sufficiently dimensioned heat storages, the heat pump can be operated gently and with maximum comfort. Cowa thermal storages are the ideal complement to heat pump systems of all kinds. The heat storage absorbs the heat from heat pumps and releases it back into the building as required. This reduces running times and protects the heat pump components. The compact cell can be used as buffer storages, domestic hot water storages or combined storages. In any installation, the technology offers a compact, hygienic and modular and scalable solution for sustainable heating systems. The Compact Cell features encompass - Compactness - Maximum comfort on a 60 x 34 cm footprint - Cubic design – The continuous, cubic housing for every corner - Hygiene – Minimum amount of standing water for highest hygienic requirements - High storage capacity – 400 l hot water production on demand - Simplicity – Sustainable heating systems in the smallest of spaces save costs and protect the climate Further information is found at the company website of Cowa at https://www.cowa-ts.com/en/products
Modular in use and with a small footprint, the scalable storage Compact Cell based on Phase Change Materials (PCM) offers maximum comfort in combination with heat pumps. Heat pumps are gaining ground worldwide. Our heat storages are designed to increase comfort in heat pump systems, reduce running times and facilitate implementation, in particular in retrofit application where space may be limited. Heat pumps extract energy from the environment and generate sustainable heat for heating and hot water. Electrically driven heat pumps generate 100% usable heat from around 20% electricity, thus conserving environmental resources. If the electricity is obtained from renewable sources, the environmental impact is further reduced. Heat pumps are versatile and are available in different configurations. By using sufficiently dimensioned heat storages, the heat pump can be operated gently and with maximum comfort. Cowa thermal storages are the ideal complement to heat pump systems of all kinds. The heat storage absorbs the heat from heat pumps and releases it back into the building as required. This reduces running times and protects the heat pump components. The compact cell can be used as buffer storages, domestic hot water storages or combined storages. In any installation, the technology offers a compact, hygienic and modular and scalable solution for sustainable heating systems. The Compact Cell features encompass - Compactness - Maximum comfort on a 60 x 34 cm footprint - Cubic design – The continuous, cubic housing for every corner - Hygiene – Minimum amount of standing water for highest hygienic requirements - High storage capacity – 400 l hot water production on demand - Simplicity – Sustainable heating systems in the smallest of spaces save costs and protect the climate Further information is found at the company website of Cowa at https://www.cowa-ts.com/en/products
Sunstore - Compact latent buffer storage for heat pumps operated with PV
A new storage concept based on macro-encapsulated PCM has been evaluated in a pilot plant over four heating periods. The salt-hydrate-based PCM capsules can be retrofitted into existing water storage tanks and, according to a material property analyses, increase the storage capacity by a factor of 2–3. In the pilot plant in Pany, GR, at an altitude of 1178 m a.s.l., the first heating period was measured using the existing water-filled buffer tank as a reference. For heating periods 2–4, different designs of PCM capsules were tested. With the increased storage capacity, the self-consumption of the installed 17 kWp PV-system is expected to rise, along with the annual performance factor, while grid dependency is reduced. The results of the heating periods with the PCM-filled storage confirm that the self-sufficiency rate (share of self-generated electricity related to the total electricity consumption) could be increased by up to 50% from 21% to 35–40%. The self-consumption rate (share of self-consumed electricity related to total PV output) was only slightly affected, as PV-output increased at the same time. Furthermore, heating demand varied highly over the four periods due to changes in occupancy and outdoor temperature, making it difficult to precisely attribute all effects. The economic viability of the capsule-based storage could not be conclusively demonstrated in this project because the comparison periods varied highly in terms of heating demand and PV yield and because future electricity tariffs play a major role. In the best case, a payback period of 12 years could be assumed based on the tariffs investigated here. An increase in the annual performance factor was not observed in the pilot plant. Consequently, the PCM storage also showed higher cycling behaviour due of the lower heat capacity in solid state of the PCM. A detailed analysis of storage behaviour shows that the storage capacity increased by up to approx. 80% compared to the water tank, and storage occurred at a lower temperature level. However, a limitation was identified: the charging and discharging performance of the PCM-filled storage is restricted by limited heat transfer between the storage water and the capsules, which reduces the use of the full capacity. This is being addressed through a new storage design. Due to lack of scalability, quality issues with the capsules, and advanced parallel development, it was decided at the beginning of 2024 not to continue the capsule concept and to replace it with a compact, fully PCM-filled storage concept – the Compact Cell. The new concept allows for very compact storage compared to water tanks. Space is often very limited, especially in renovation projects, and installing a sufficiently large buffer tank is not always possible. An undersized tank can cause problems such as excessive cycling (reducing lifetime of the components). The Compact Cell provides a solution by offering sufficient storage capacity in a small space. Furthermore, a domestic hot water tank is integrated into the concept, which significantly expands the application range . The final report (in German) can be accessed at the link https://www.aramis.admin.ch/Default?DocumentID=73992&Load=true Authors: Christoph Meier, Carsten Wemhoener, Marc Werro, Bercan Siyahhan, Philipp Roos, Roger Zimmermann, Remo Waser Note: The pilot plant measurements of the capsule storage concept was performed outside the Renowave project.
A new storage concept based on macro-encapsulated PCM has been evaluated in a pilot plant over four heating periods. The salt-hydrate-based PCM capsules can be retrofitted into existing water storage tanks and, according to a material property analyses, increase the storage capacity by a factor of 2–3. In the pilot plant in Pany, GR, at an altitude of 1178 m a.s.l., the first heating period was measured using the existing water-filled buffer tank as a reference. For heating periods 2–4, different designs of PCM capsules were tested. With the increased storage capacity, the self-consumption of the installed 17 kWp PV-system is expected to rise, along with the annual performance factor, while grid dependency is reduced. The results of the heating periods with the PCM-filled storage confirm that the self-sufficiency rate (share of self-generated electricity related to the total electricity consumption) could be increased by up to 50% from 21% to 35–40%. The self-consumption rate (share of self-consumed electricity related to total PV output) was only slightly affected, as PV-output increased at the same time. Furthermore, heating demand varied highly over the four periods due to changes in occupancy and outdoor temperature, making it difficult to precisely attribute all effects. The economic viability of the capsule-based storage could not be conclusively demonstrated in this project because the comparison periods varied highly in terms of heating demand and PV yield and because future electricity tariffs play a major role. In the best case, a payback period of 12 years could be assumed based on the tariffs investigated here. An increase in the annual performance factor was not observed in the pilot plant. Consequently, the PCM storage also showed higher cycling behaviour due of the lower heat capacity in solid state of the PCM. A detailed analysis of storage behaviour shows that the storage capacity increased by up to approx. 80% compared to the water tank, and storage occurred at a lower temperature level. However, a limitation was identified: the charging and discharging performance of the PCM-filled storage is restricted by limited heat transfer between the storage water and the capsules, which reduces the use of the full capacity. This is being addressed through a new storage design. Due to lack of scalability, quality issues with the capsules, and advanced parallel development, it was decided at the beginning of 2024 not to continue the capsule concept and to replace it with a compact, fully PCM-filled storage concept – the Compact Cell. The new concept allows for very compact storage compared to water tanks. Space is often very limited, especially in renovation projects, and installing a sufficiently large buffer tank is not always possible. An undersized tank can cause problems such as excessive cycling (reducing lifetime of the components). The Compact Cell provides a solution by offering sufficient storage capacity in a small space. Furthermore, a domestic hot water tank is integrated into the concept, which significantly expands the application range . The final report (in German) can be accessed at the link https://www.aramis.admin.ch/Default?DocumentID=73992&Load=true Authors: Christoph Meier, Carsten Wemhoener, Marc Werro, Bercan Siyahhan, Philipp Roos, Roger Zimmermann, Remo Waser Note: The pilot plant measurements of the capsule storage concept was performed outside the Renowave project.


